DNA Barcoding of Hemerodromia Meigen, 1822 (Diptera: Empididae) from Thailand
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58837/tnh.21.2.251305Keywords:
cytochrome c oxidase I, DNA barcode, Empididae, Hemerodromia, ThailandAbstract
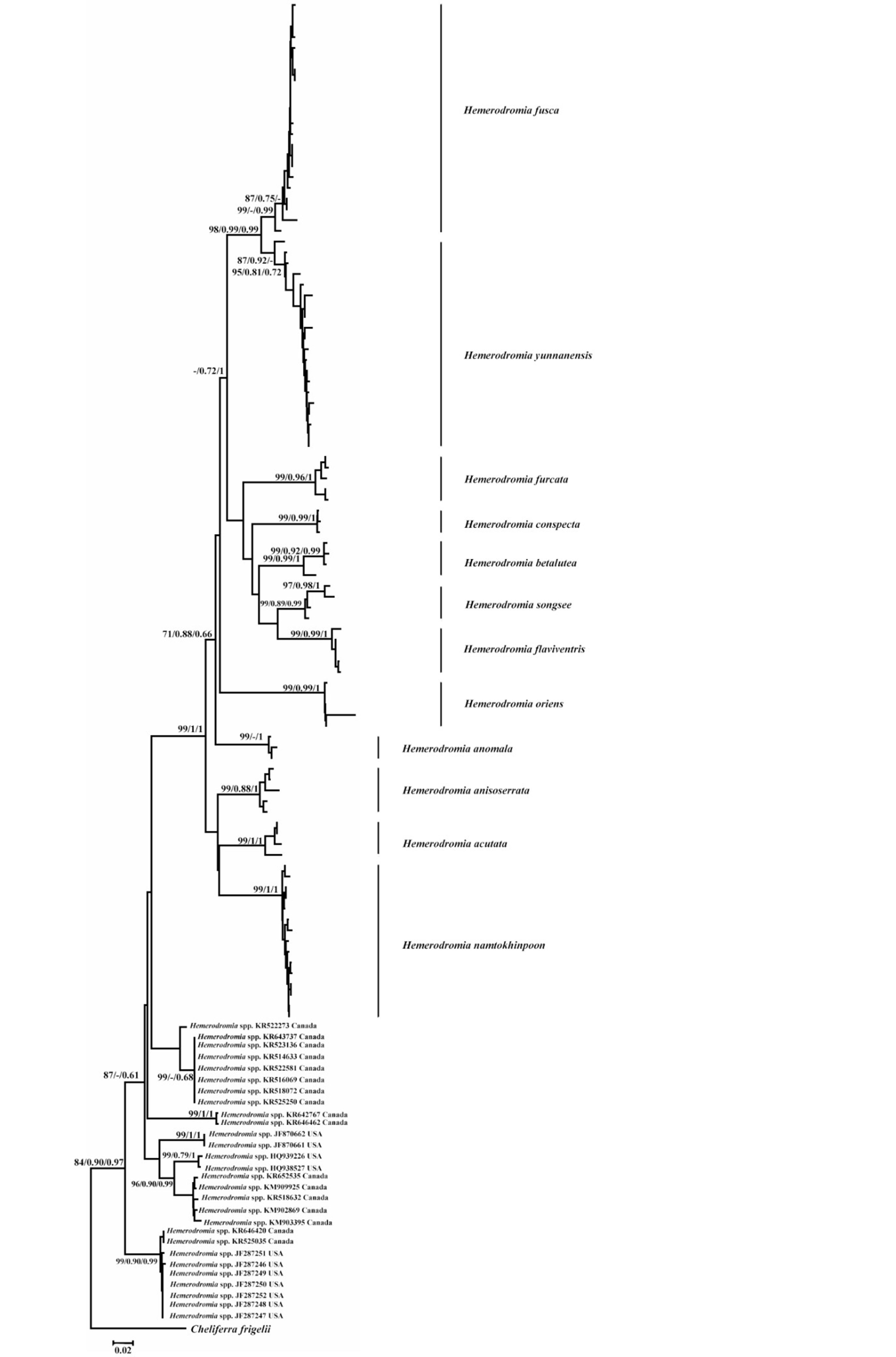
Species of Hemerodromia Meigen, 1822 (Diptera, Empididae, Hemerodromiinae) are important components of lotic habitats in freshwater ecosystems. The goal of this study was to test the efficiency of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) barcoding region for species level identification of Hemerodromia in Thailand. Twelve Hemerodromia species were collected from 31 sites in North and Northeastern Thailand and 135 COI sequences obtained. DNA barcoding identification analysis based on the best close match method performed well; with 100% of specimens agreeing with morphological identification. A phylogenetic tree based on the 135 mitochondrial barcode sequences obtained here and 28 sequences from the NCBI database revealed a well-supported monophyly for all Hemerodromia species from Thailand.
References
Changbunjong, T., Bhusri, B., Sedwisai, P., Weluwanarak, T., Nitiyamatawat, E., Chareonviriyaphap, T. and Ruangsittichai, J. 2018. Species identification of horse flies (Diptera: Tabanidae) in Thailand using DNA barcoding. Veterinary Parasitology, 259: 35-43.
Folmer, O., Black, M., Hoeh, W., Lutz, R. and Vrijenhoek, R. 1994. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3: 294-299.
Guindon, S., Dufayard, J.F., Lefort, V., Anisimova, M., Hordijk, W. and Gascuel, O. 2010. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Systematic Biology, 59: 307-321.
Hajibabaei, M., Singer, G.A.C., Hebert, P.D.N. and Hickey, D.A. 2007. DNA barcoding: how it complements taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics and population genetics. Trends in Genetics, 23: 167-172.
Huelsenbeck, J.P. and Ronquist, F.R. 2001. MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogeny. Bioinformatics, 17: 754-755.
Ivković, M., Kepčija, R.M., Mihaljević, Z., and Horvat, B. 2007. Assemblage composition and ecological features of aquatic dance flies (Diptera, Empididae) in the Cetina River system, Croatia. Fundamental and Applied Limnology-Archiv fur Hydrobiologie, 170: 223-232.
Knutson, L.V. and Steyskal, G.C. 1981. Empididae. In: McAlpine, J.F. Peterson, G.E. Shewell, G.E. Teskey, H.J. Vockeroth, J.R. and Wood, D.M. (Eds.). Manual of Nearctic Diptera, Volume 1, Agriculture Canada Monograph, 27, Research Branch Agriculture Canada, Ottawa, pp. 607-624.
Kondo, N.I., Ueno, R., Ohbayashi, K., Golygina, V.V. and Takamura, K. 2016. DNA barcoding supports reclassification of Japanese Chironomus species (Diptera: Chironomidae). Entomological Science, 19: 337-350.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G.Li.M., Knyaz, C. and Tamura, K. 2018. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35: 1547-1549.
Kunprom, C. and Pramual, P. 2016. DNA barcode variability and host plant usage of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Thailand. Genome, 59: 792-804.
Kunprom, C., Plant, A.R. and Pramual, P. 2021. Population genetic structure and microendemism in aquatic Empididae (Diptera) in transient tufa biotopes on tropical karst. Entomological Science. 24: 127–136.
Meier, R. Shiyang, K. Vaidya, G. and Ng, P.K.L. 2006. DNA barcoding and taxonomy in Diptera: a tale of high intraspecific variability and low identification success. Systematic Biology, 55: 715-728.
Nagy, Z.T., Sonet, G., Mortelmans, J., Vandewynkel, C. and Grootaert, P. 2013. Using DNA barcodes for assessing diversity in the family Hybotidae (Diptera, Empidoidea). ZooKeys, 365: 263.
Nylander, J.A.A. 2004. MrModeltest 2.2. Program Distributed by the Author.Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
Plant, A.R. 2011. Hemerodromiinae (Diptera: Empididae), a tentative phylogeny and biogeographical discussion. Systematic Entomology, 36: 83-103.
Plant, A.R. 2015. Diversity of Hemerodromia Meigen, 1822 (Diptera: Empididae) in Thailand, the tip of a tropical iceberg? Zootaxa, 4039: 001-056.
Plant, A.R. 2020. New species of Hemerodromia Meigen (Diptera: Empididae: Hemerodromiinae) associated with limestone karstic waters in Thailand. Zootaxa, 4758: 549-560.
Plant, A.R. 2021. Tropical tufa and karst streams support unique and threatened assemblages of aquatic Diptera, Empididae in Thailand. Entomological Science. 24: 169–182.
Pramual, P. and Adler, P.H. 2014. DNA barcoding of tropical black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) of Thailand. Molecular Ecology Resources, 14: 262-271.
Pramual, P. and Pangjanda, S. 2015. Effects of habitat specialization on population genetic structure of black fly Simulium weji Takaoka (Diptera: Simuliidae). Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 18: 33-37.
Pramual, P., Thaijarern, J. and Wongpakam, K. 2016. DNA barcoding of human-biting black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Thailand. Acta Tropica, 164: 33-40.
Rivera, J. and Currie, D.C. 2009. Identification of Nearctic black flies using DNA barcodes (Diptera: Simuliidae). Molecular Ecology Resources, 9: 224-236.
Thaijarern, J., Pramual, P. and Adler, P.H. 2017. Life-stage association of black flies, using a fast-evolving nuclear gene sequence, and description of the larva of Simulium lampangense Takaoka & Choochote (Diptera: Simuliidae) from Thailand. Zootaxa, 4299: 263-270.
Wagner, R., Leese, F. and Panesar, A.R. 2004. Aquatic dance flies from a small Himalayan mountain stream (Diptera: Empididae: Hemerodromiinae: Trichopezinae and Clinocerinae). Bonner Zoologische Beiträge, 52: 3-32.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Chulalongkorn University. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, translated, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without prior written permission of the publisher











