Morphological Observation on Physaloptera Species (Nematoda: Spirurida: Physalopteridae) in Murine Rodents of Indonesia and East Asian Islands with Special Reference to Their Zoogeographical Features
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58837/tnh.22.1.257331Keywords:
Physaloptera, Maxomys, Apodemus, Rattus, insular distribution, morphology, dispersalAbstract
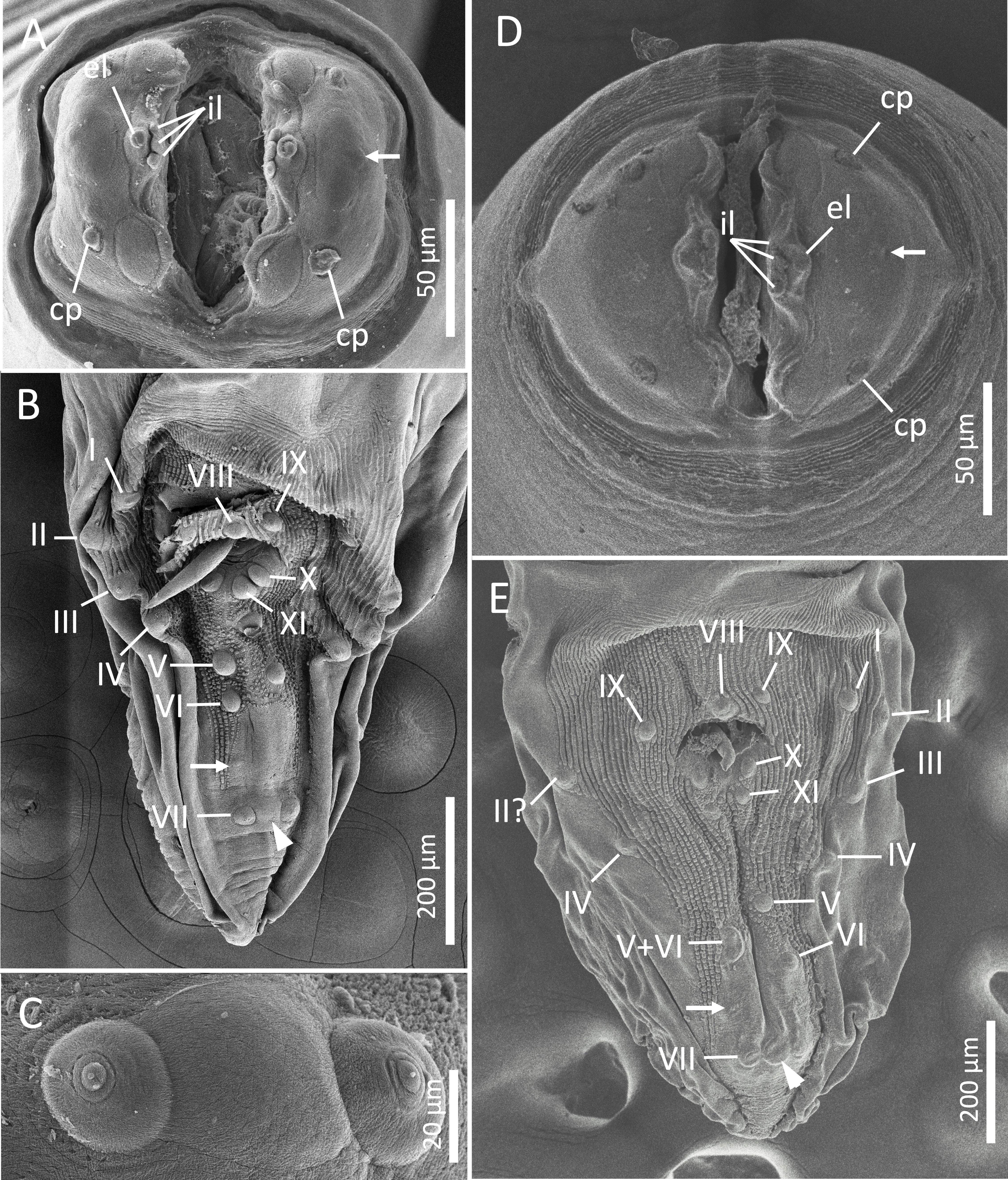
Morphological observations of specimens from the genus Physaloptera spp. (Spirurida: Physalopteridae) collected from murine species in Indonesia and some islands of East Asia were made. The physalopterid worms found from Maxomys whiteheadi and Maxomys bartelsii of Kalimantan and West Java, Indonesia, respectively, Apodemus speciosus of the Izu Islands, Japan, Apodemus agrarius of Jeju Island, Korea, and Rattus tanezumi of Uotsuri Island, in the Senkaku Islands, Japan, were identified as P. apodemi Wang & Zhang, 2020, previously only reported from Tianjin, China. On the other hand, those in Rattus argentiventer of West Java were identified with P. ngoci Le-Van-Hoa, 1961 as the first geographical record outside of the continental portion of Southeast Asia. Supplemental morphological remarks were made for P. apodemi with special attention to the differentiation from other congeners. The distribution of P. apodemi on these small remote islands suggests that dispersal occurred accidentally via synanthropic rats and/or intermediate host insects that possibly escaped from shipwrecks onto these islands.
References
Alcántara, M. 1991. Geographical variation in body size of the wood mouse Apodemus sylvaticus L. Mammal Review, 21: 143–150.
Asakawa, M. 1997. Zoogeography on parasites of Japanese rodents. Journal of Japanese Wildlife Research Society, 23: 30–42. (in Japanese)
Asakawa, M. and Hasegawa, H. 2018. Redescription of Heligmonoides vladimiri Sadovskaja, 1952 (Nematoda: Heligmonellidae: Nippostrongylinae) parasitic in the striped field mouse, Apodemus agrarius (Rodentia: Muridae), of the Far East. Biogeography, 20: 34–40.
Ash, L. R. 1962. The helminth parasites of rats in Hawaii and the description of Capillaria traverae sp. n. Journal of Parasitology, 48: 66–68.
Bird, M. I., Taylor, D. and Hunt, C. 2005. Paleoenvironments of insular Southeast Asia during the last glacial period: a savanna corridor in Sundaland? Quaternary Science Reviews, 24: 2228–2242.
Chabaud, A. G. 1956. Essai de révision des physaloptères parasites de reptiles. Annals de Parasitologie, 31: 29–52.
Chabaud, A. G. 1975. Keys to Genera of the Order Spirurida, Part I. Camallanoidea, Dracunculoidea, Gnathostomatoidea, Physalopteroidea, Rictularioidea and Thelazioidea. In: Anderson, R. C., Chabaud, A. G. and Willmott, S. (Eds) CIH Keys to the Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. No. 3. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Farnham Royal, Buckinghamshire, England, 27 pp.
Charleston, W. A. G. and Innes, J. G. 1980. Seasonal trends in the prevalence and intensity of spiruroid nematode infections of Rattus r. rattus. New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 7: 141–145.
Dewi, K., Hasegawa, H. and Asakawa, M. 2018. Redescription of Subulura (Murisubulura) andersoni (Cobbold, 1876) (Nematoda: Subuluridae) from Bunomys spp. (Rodentia: Muridae) of Sulawesi, Indonesia, with special reference to S. (M.) suzukii and other related species in the adjacent areas. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 80: 1639–1645.
Ederli, N. B., Gallo, S. S. M., Oliveira, L. C. and Rodrigues de Oliveira, F. C. 2018. Description of a new species Physaloptera goytaca n. sp. (Nematoda, Physalopteridae) from Cerradomys goytaca Tavares, Pessôa & Gonçalves, 2011 (Rodentia, Cricetidae) from Brazil. Parasitology Research, 117: 2757–2766.
Harper, G. A. and Bunbury, N. 2015. Invasive rats on tropical islands: Their population biology and impacts on native species. Global Ecology and Conservation, 3: 607–627.
Hasegawa, H., Shiraishi, S. and Rochman. 1992. Tikusnema javaense n. gen., n. sp. (Nematoda: Acuarioidea) and other nematodes from Rattus argentiventer collected in West Java, Indonesia. Journal of Parasitology, 78: 800-804.
Hasegawa, H., Arai, S. and Shiraishi, S. 1993. Nematodes collected from rodents on Uotsuri Island, Okinawa, Japan. Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 60: 39-47.
Johnston, T. H. and Mawson, P. M. 1941. Some parasitic nematodes in the collection of the Australian Museum. Records of the Australian Museum, 21: 9–16.
Koh, H. S., Shaner, P. J., Csorba, G., Wang, Y. J., Kyung, H. and Lee, J. H. 2014. Comparative genetics of Apodemus agrarius (Rodentia: Mammalia) from insular and continental Eurasian populations: Cytochrome b sequence analyses. Acta Zoologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 60: 73–84.
Kontrimavichus, W. L. and Chochlowa, I. G. 1964. On the question оf the effect of food upon composition and dynamics of the helminth fauna оf rodents. Helminthologia, 5: 197–215.
Latinne, A., Navascués, M., Pavlenko, M., Kartavtseva, I., Ulrich, R. G., Tiouchichine, M.-L., Catteau, G., Sakka, H., Quéré, J. P., Chelomina, G., Bogdanov, A., Stanko, M., Hang, L., Neumann, K., Henttonen, H. and Michaux, J. 2020. Phylogeography of the striped field mouse, Apodemus agrarius (Rodentia: Muridae), throughout its distribution range in the Palaearctic region. Mammalian Biology, 100: 19–31.
Le-Van-Hoa, 1961. Etude d’un nouveau Physaloptère du rat, trouvé au Viet-Nam. Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée, 36: 672–676.
Lee, Y. I., Pyeon, H. J. and Seo, M. 2013. Intestinal parasites among wild rodents in Northern Gangwon-do, Korea. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 51: 603–606.
Maldonado, A. Jr., Simões, R. O., Saõ Luiz, J. S., Costa-Neto, S. F. and Vilela, S. F. 2019. A new species of Physaloptera (Nematoda: Spirurida) from Proechimys gardneri (Rodentia: Echimyidae) from the Amazon rainforest and molecular phylogenetic analyses of the genus. Journal of Helminthology, 94: e68.
Morgan, B. B. 1943. The Physaloptera (Nematoda) of rodents. Wasmann Collector, 5: 99–107.
Mosby, J. M. and Wodzicki, K. 1972. Some parasites of the Kimoa (Rattus exulans) on the Tokelau Islands. New Zealand Journal of Science, 15: 698–704.
Musser, G. G. and Carleton, M. D. 2005. Superfamily Muroidea. In: Wilson, D.E. and Reeder, D.M. (Eds) Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 2142 pp.
Norman, R. J. de B. and Beveridge, I. 1999. Redescriptions of the species of Physaloptera Rudolphi, 1819 (Nematoda: Spirurida) parasitic in bandicoots (Marsupialia: Perameloidea) in Australia. Systematic Parasitology, 43: 103–121.
Ohdachi, S. D., Ishibashi, Y., Iwasa, M. A., Fukui, D. and Saitoh, T. (Eds) 2015. The Wild Mammals of Japan (2nd ed.), Shoukadoh, Kyoto, Japan. 506 pp.
Ortlepp, R. J. 1922. The nematode genus Physaloptera Rudolphi. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London, 4: 999–1107.
Pereira, F. B., Alves, P. V., Rocha, B. M., Lima, S. S. and Luque, J. L. 2012. A new Physaloptera (Nematoda: Physalopteridae) parasite of Tupinambis merianae (Squamata: Teiidae) from southwestern Brazil. Journal of Parasitology, 98: 1227–1235.
Quentin, J. C. 1968. Physaloptera longispicula nouvelle espèce de Spiruride parasite de Cercomys cunicularius Cuvier. Bulletin de la Muséum Nationale d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, 2e Sér. 40: 1043–1046.
Roberts, M. 1991. The parasites of the Polynesian rat: Biogeography and origins of the New Zealand parasite fauna. International Journal for Parasitology, 21: 785–793.
Sakata, K., Takada, Y., Uematsu, Y., Sakai, E., Tateishi, T., Hasegawa, M., Kageyama, M. and Asakawa, M. 2006. The first report of parasitic nematodes obtained from the large Japanese field mice, Apodemus speciosus (Muridae, Rodentia) collected on the Izu Islands, Japan, with a brief zoogeographical comment for its nematode fauna. Bulletin of the Biogeographical Society of Japan, 61: 135 – 139. (in Japanese)
São Luiz, J., Simões, R. O., Torres, E. L., Barbosa, H. S., Santos, J. N., Giese, E. G., Rocha, F. L. and Maldonado, A., Jr. 2015. A new species of Physaloptera (Nematoda: Physalopteridae) from Cerradomys subflavus (Rodentia: Sigmodontinae) in the Cerrado Biome, Brazil. Neotropical Helminthology, 9: 301–312.
Schell, S. C. 1950. A new species of Physaloptera (Nematoda: Spiruroidea) from the cotton rat. Journal of Parasitology, 36: 423–425.
Seo, B. S., Rim, H. J., Yoon, J. J., Koo, B. Y. and Hong, N. T. 1968. Studies on the parasitic helminths of Korea III. Nematodes and cestodes of rodents. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 6: 123–131.
Seurat, L. G. 1917. Physaloptères des mammifères du Nord Africain. Comptes Rendus de la Société de Biologie, 80: 210–218.
Seurat, G. 1937. Sur quelques nématodes de l’estomac des muridés et les réactions qu’ils provoquent. Bulletin de la Société d’Histoire Naturelle de Afrique Nord, 28: 428–431.
Skrjabin, K. I. and Sobolev, A. A. 1964. Spirurata of Animals and Man and the Diseases Caused by Them. Part 2. Physalopteroidea. In: Skrjabin, K. I. (Ed.) Osnovi Nematodologi 12. Izdatel’stvo Akademii Nauka, Moscow, 195 pp. (in Russian)
Smales, L. R. 2005. Helminth parasites of the grassland melomys (Muridae: Hydromyinae) from Australia and Papua New Guinea. Australian Journal of Zoology, 53: 369–374.
Sohn, W. M., Na, B. K., Song, H. J., Kim, C. M. and Nam, G. J. 2014. Intestinal helminthic infections in striped field mice, Apodemus agrarius, from two southern regions of Korea. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 52: 419–423.
Sutton, C. A. 1989. Contribution to the knowledge of Argentina's parasitological fauna XVII. Spirurida (Nematoda) from Neotropical Cricetidae: Physaloptera calnuensis n. sp. and Protospirura numidica criceticola Quentin, Karimi and Rodriguez de Almeida. Bulletin de la Muséum Nationale d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, 4e sér., 11, section A, no. 1: 61–67.
Suzuki, H., Yasuda, S. P., Sakaizumi, M., Wakana, S., Motokawa, M. and Tsuchiya, K. 2004. Differential geographic patterns of mitochondrial DNA variation in two sympatric species of Japanese wood mice, Apodemus speciosus and A. argenteus. Genes & Genetic Systems, 79: 165–176.
Swanson, L. E. 1939. A note on the parasite fauna of the Hawaiian Islands. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 6: 29–30.
Takada, Y., Sakai, E., Uematsu, Y. and Tateishi, T. 2006. Morphological variation of large Japanese field mice, Apodemus speciosus on the Izu and Oki Islands. Mammal Study, 31: 29–40.
Travassos, L. 1920. Contribuições para o conhecimento da fauna helmintolojica brasileira - X. Sobre as especies do genero Turgida. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 12: 73–77.
Vaz, Z. and Pereira, C. 1935. Some new Brazilian nematodes. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 54: 36–40.
Veciana, M., Chaisiri K., Morand, S., Miquel, J. and Ribas, A. 2013. New biogeographical and morphological information on Physaloptera ngoci Le-Van-Hoa, 1961 (Nematoda: Physalopteridae) in South-east Asian rodents. Parasite, 20: 23.
Wang, Y. and Zhang, L. 2020. Physaloptera apodemi sp. nov. (Nematoda: Physalopteridae) from Apodemus sylvaticus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Rodentia: Muridae) from Tianjin, China. Zoological Systematics, 45: 259–265.
Wiroreno, W. 1978. Nematode parasites of rats in West Java, Indonesia. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 9: 520–525.
Zhang, N. X. 1985. Two new hosts of Physaloptera mustelae. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 10: 233. (in Chinese)
Zhang, N. X. and Yin, W. Z. 1980. On some parasitic helminths of yellow weasel from China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 5: 232–234. (in Chinese)
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Chulalongkorn University. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, translated, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without prior written permission of the publisher











