Health Literacy and Predicting Factors to Controlled Blood Sugar Levels among Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Boonsurb Sosome
Keywords:
Gestational diabetes, Health literacy, Blood sugar controlAbstract
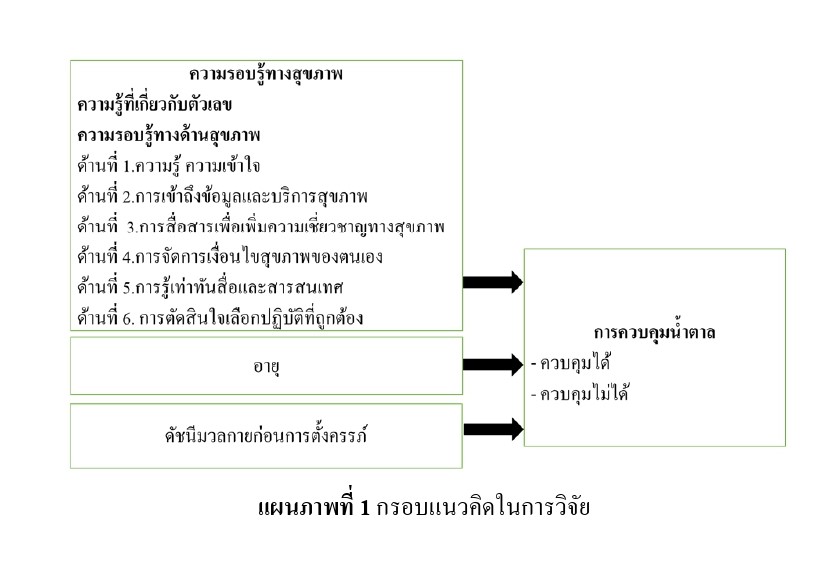
This descriptive cross-sectional study was aimed to study health literacy and factors predicting blood glucose control level among Thai pregnant women with gestational diabetes. The sample was 171 Thai pregnant women with gestational diabetes, followed up at the prenatal clinic. The research instrument consisted of 2 parts. The firstly was demographic data and obstetrics questionnaires and blood sugar level record. The secondly was the Health Literacy scale, including of health literacy on numeric and Nutbeam’s health literacy concept in which CVI were .92, and .98 and reliabilities, Cronbach’s alpha were .70 and .93 respectively. Data were analyzed by using descriptive statistics and Logistic regression. The results demonstrated the mean score of health literacy on numeric is at a high level (M = 6.80, S.D. = 2.19), health literacy on Nutbeam’s concept is at a high level (M = 3.85, S.D. = .46), the communication to potential improve patient health dimension is the highest score (M = 4.07, S.D. = .36). The access to health data and service was the predicted factors for controlled blood sugar on women with gestational diabetes mellitus (odds ratio = 2.41, p =.04). The recommendation from the results is that multidisciplinary should effectively promote access to health information and service.
References
Berkman, N.D., Sheridan, S.L., Donahue, K.E., Halpern, D.J., & Crotty, K. (2011). Low health literacy and health outcomes: An updated systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine, 155(2), 97 - 107. DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-00005.
Best, J.W. (1977). Research in education. (2nd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice–Hall.
Bootsri, W., & Sirisophon, A. (2020). Predicting Factors of Promoting Behaviors among Pregnant Women Receiving Antenatal Care Services at Community Hospital, Nakhonsawan Province. Journal of Allied Health Sciences Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, 5(1), 60 - 70.
Diabetic Association of Thailand, The Endocrine Society of Thailand, Institute of Medical Research and Technology Assessment, Department of Medical Service, National Health Security Office. (2017). Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes, Prathum Thani: Royen Media Company Limited. (in Thai)
Forghani, T., Ahmadian, M., Rezaeisharif, F., & Ahadi, M. (2021). Survey of health literacy during pregnancy and its relationship with prenatal care. Journal of Health Literacy, 6(1), 20 - 30.
Gharachourlo, M., Mahmoodi, Z., Akbari Kamrani, M., Tehranizadeh, M., & Kabir, K. (2018). The effect of a health literacy approach to counselling on the lifestyle of women with gestational diabetes: A clinical trial. F1000Research, 7, 282. DOI:10.12688/f1000research.13838.1.
Jangsavang, S., Siriarunrat, S., & Tachasuksri,T. (2020). Factors predicting blood glucose control behavior among pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. The Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 28(3), 79 - 89.
Jovanovic-Peterson, L., & Peterson, C.M. (1996). Review of gestational diabetes mellitus and low-calorie diet and physical exercise as therapy. Diabetes/metabolism reviews, 12(4), 287 - 308. DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0895(199612)12:4<287::AID-DMR170>3.0.CO;2-E
Kharrazi, S.S., Peyman, N., & Esmaily, H. (2018). Correlation between maternal health literacy and dietary self-efficacy in pregnant mothers. Health Education and Health Promotion, 6(1), 9 - 16.
Lee, K.W., Ching, S.M., Ramachandran, V., Yee, A., Hoo, F.K., Chia, Y.C., … Veettil, S.K. (2018). Prevalence and risk factors of gestational diabetes mellitus in Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth, 18, 494 DOI:10.1186/s12884-018-2131-4
Long, J.S. (1997). Regression Models for categorical and limited dependent variables. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications
Lupattelli, A., Picinardi, M., Einarson, A. & Nordeng, H. (2014). Health Literacy and Its Association with Perception of Teratogenic RIsks and Health Behavior During Pregnancy. Patient Education and Counseling, 96(2), 171 - 178.
McKenzie-Sampson, S., Paradis, G., Healy-Profitós, J., St-Pierre, F., & Auger, N. (2018). Gestational diabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease up to 25 years after pregnancy: A retrospective cohort study. Acta Diabetologica, 55(4), 315 - 322. DOI:10.1007/s00592-017-1099-2.
Mohamady, S.H., Abd Elmoneim, S.O., & Abdelhakam, E.M. (2022). Effect of counseling program based on health literacy model regarding gestational diabetes on maternal and fetal outcomes. Tanta Science Nursing Journal, 26(3), 181 - 203.
Mojoyinola, J.K. (2011). Influence of Maternal Health Literacy on Healthy Pregnancy and Pregnancy Outcomes of Women Attending Public Hospitals in Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria. An International Multi-Disciplinary Journal Ethiopia, 5(3), 28 - 39.
Muche, A.A., Olayemi, O.O., & Gete, Y.K. (2020). Effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on risk of adverse maternal outcomes: A prospective cohort study in Northwest Ethiopia. BMC regnancy and Childbirth, 20(1), 73. DOI:10.1186/s12884-020-2759-8.
Nawabi, F., Alayli, A., Krebs, F., Lorenz, L., Shukri, A., Bau, A. M., & Stock, S. (2021). (a). Health literacy among pregnant women in a lifestyle intervention trial: Protocol for an explorative study on the role of health literacy in the perinatal health service setting. BMJ Open, 11(7), e047377.
Nawabi, F., Krebs, F., Vennedey, V., Shukri, A., Lorenz, L., & Stock, S. (2021). (b). Health literacy in pregnant women: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3847.
Nutbeam, D. (2000). Health literacy as a public goal: A challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International, 15(3), 259 - 267. DOI:10.1093/heapro/15.3.259.
Panmuang, S., & Amatayabundit, N. (2022). Effective factors associated with blood sugar among gestational diabetes mellitus at Mahasarakham hospital. Journal of MCU Nakhondhat, 9(4), 278 - 291.
Parnell, A. S., Correa, A., & Reece, E. A. (2017). Pre-pregnancy obesity as a modifier of gestational diabetes and birth defects associations: A systematic review. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 21(5), 1105 - 1120. DOI:10.1007/s10995-016-2209-4.
Pirdehghan, A., Eslahchi, M., Esna-Ashari, F., & Borzouei, S. (2020). Health literacy and diabetes control in pregnant women. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 9(2), 1048 - 1052. DOI:10.4103/jfmpc. jfmpc891_19.
Pornkuna, W., Wenuka, & Anusornteerakul, S. (2017). The effects of program on knowledge, blood sugar level control and re-admission of women with insulin-dependent gestational diabetes mellitus. Srinagarind Medical Journal, 32(2), 135 - 142.
Ratarasarn, C. (2017). Current situation and cooperation to reform diabetes care in Thailand. Retrieved January 31, 2020 from https://www.novonordiskcontent/dam/Denmark/HQ/ sustainablebusiness/performance-on-tbl/more-about-how-we-work/Creating%20shared%20 valuePDF/Thailand%20Blueprint %20for%20Change_2017TH.pdf.
Rattanawarang, W., & Chantha, W. (2018). Health literacy of self-care behaviors for blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes, Chainat province. The Journal of Baromarajonani College of Nusing Nakhonratchasima, 24(2), 34 - 51.
Rawal, S., Olsen, S.F., Grunnet, L.G., Ma, R.C., Hinkle, S.N., Granström, C., … Zhang, C. (2018). Gestational diabetes mellitus and renal function:a prospective study with 9- to 16-year follow-up after pregnancy. Diabetes Care, 41, 1378 - 1384. DOI: 10.2337/dc17-2629.
Singwongsa, A., & Boriboonhirunsarn, D. (2016). Incidence and associated factors of gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosed during 24-28 weeks of gestation. Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 24, 184 - 192.
Sosome, B., Wimonmala, K., Suwannaka, Y., & Howharn, C. (2021). Promoting Health Literacy: The Essential Care for Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in COVID-19 Era. Royal Thai Navy Medical Journal, 48(1), 224 - 240.
Stevens, J. (1996). Applied Multivariate Statistics for the Social Sciences. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Tachasuksri, T., Siriarunrat, S., Suppasri, P., Suppaseemanont, W., Boonnate, N., & Kwannate, C. (2017). Causal model for quality of life among pregnant women. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 4(1), 28 - 46.
Taherdoost, H. (2017). Determining sample size; how to calculate survey sample size. Leadership & Organizational Behavior eJournal. Retrieved January 20, 2020 from SSRN: https://ssrn .com/abstract=2984854.
Tharavanij, T. (2021). Women with diabetic. Retrieved January 20, 2020 from https://www.thaihealth.or.th.
Uthaithum, N., Gettong1, N., & Somjai C. (2021). Factors predicting health literacy of pregnant women. Journal of Prachomklao College of Nursing, Phetchaburi Province, 4(2), 53 - 56.
Waraphok, S., Ratinthorn, A., & Limruangrong, P. (2020). Factors Influencing Maternal Health Literacy in Pregnant Women. Journal of Thailand Nursing and Midwifery Council, 35(1), 86 - 98.
Werner, E. F., Romano, M. E., Rouse, D. J., Sandoval, G., Gyamfi-Bannerman, G., Blackwell, S., … Sorokin, Y. (2019). Association of gestational diabetes mellitus with neonatal respiratory morbidity. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 133(2), 349 - 353. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003053.
Xu, H.B., Li, M.H., Tang, X.F., & Lu, J. (2022). The relationship between poor glycaemic control at different time points of gestational diabetes mellitus and pregnancy outcomes. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 42(7), 2979 - 2986. DOI:10.1080/01443615.2022.2124852
Yee, L.M., Silver, R., Haas, D.M., Parry, S., Mercer, B.M., Wing, D.A., ... Grobman, W.A. (2021). Association of health literacy among nulliparous individuals and maternal and neonatal outcomes. JAMA Network Open, 4(9), e2122576.
Zhang, Z. (2016). Model building strategy for logistic regression: purposeful selection. Annals of Translational Medicine. 4(6), 111. DOI:10.21037/atm.2016.02.15
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



