Factors Affecting Drug Relapse in Persons with Mixed Type Drug Addiction: A Systematic review
Keywords:
Drug relapse, Drug addicted persons, Mixed type drug addiction, A systematic reviewAbstract
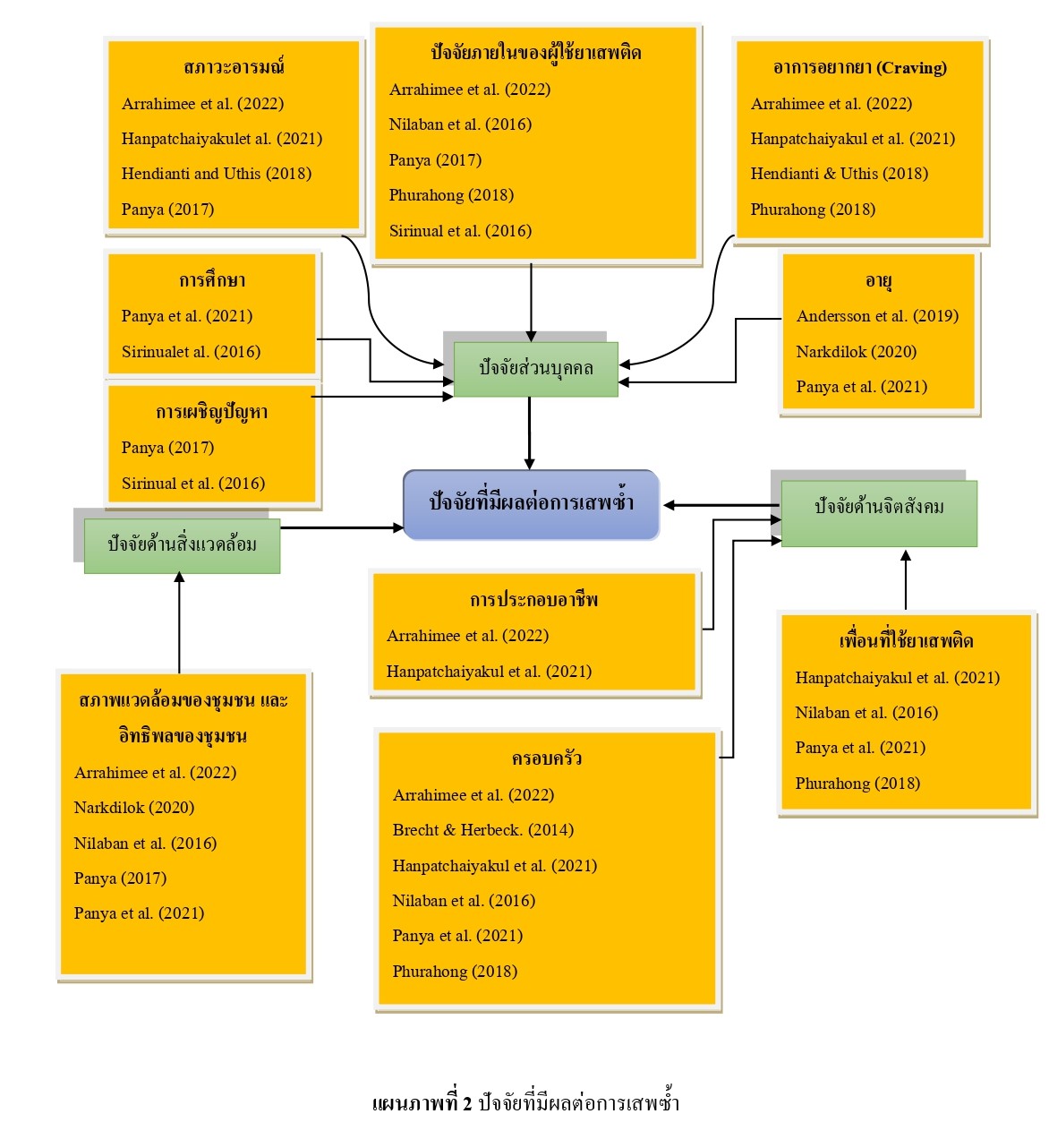
This systematic review aimed to identify, analyze, and synthesize the factors affecting drug relapse in persons with mixed type drug addiction using a combination of methamphetamine and other drugs through all available literature from 2014 to 2023. Research critical appraisal and data extraction were conducted by a data extraction form produced by The Joanna Briggs Institute. According to the search results, 256 papers from 8 databases examined factors affecting drug relapse among drug addicted patients with mixed type drug addiction. A total of 245 studies were eliminated due to their incompatibility with the inclusion criteria. Merely eleven studies satisfied all the inclusion criteria. Eight studies were conducted in Thailand and three studies were conducted overseas. There were five relationship studies, two exploration studies, one mixed method study, one cohort study, and two qualitative research studies. Research findings and knowledge synthesis of the factors affecting drug relapse in persons with mixed type drug addiction were descriptive in characterizing the factors and their relationship to drug relapse. The findings indicated that among patients with mixed-type drug addiction, factors influencing drug relapse included age, educational attainment, signs of drug craving, psychological factors such as friends, family, and occupation of drug addicts, and environmental factors such as neighborhood environment and community influence. The findings can be used to conduct research and create guidelines for preventing drug relapse through increased collaboration between the multidisciplinary team, family, and community.
References
Andersson, H.W., Wenaas, M., & Nordfjærn, T. (2019). Relapse after inpatient substance use treatment: A prospective cohort study among users of illicit substances. Addictive Behaviors, 90, 222 – 228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.11.008
Arrahimee, A., Saengthong, T., Jeawkok, J., & Laipaporne, S. (2022). Self-prevention against drug abise relapse: A case study of people undergoing drug addiction treatment in Pattani province. Journal of community development and life quality, 10(1), 345 - 357. http://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JCDLP/article/view/254736
Brecht, M.L., & Herbeck, D. (2014). Time to relapse following treatment for methamphetamine use: A long-term perspective on patterns and predictors. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 139, 18 – 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.02.702
Hanpatchaiyakul, K., Kasemporn, N., Thoin, P., & Thongkote, N. (2021). Factors affecting the readmission of patients recovering from drug addiction. Journal of health science research, 15(2), 1 – 12. http://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JHR/article/view/247142
Hendianti, G.N., & Uthis, P. (2018). Factors related to methamphetamine relapse risk among clients in the substance rehabilitation center of National Narcotics Board in West Java, Indonesia. Journal of Health Research, 32(4), 279 – 287. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHR-05-2018-035
Kakko, J., Alho, H., Baldacchino, A., Molina, R., Nava, F.A., & Shaya, G. (2019). Craving in Opioid Use Disorder: From Neurobiology to Clinical Practice. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 592. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00592
Kuypers, K., Verkes, R., van den Brink, W., van Amsterdam, J., & Ramaekers, J. (2020). Intoxicated aggression: Do alcohol and stimulants cause dose-related aggression? A review. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 30, 114 – 147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.06.001
Marlatt, G. A., & Donovan, D. M. (2005). Relapse prevention: Maintenance strategies in the treatment of addictive behaviors (2nd ed.). The Guilford Press. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/ 2005-08721-000
Ministry of Public Health. (2023, December 1). National drug addiction treatment and rehabilitation information system. Office of the Secretary of the Drug Addiction Treatment and Rehabilitation Committee. https://antidrugnew.moph.go.th.
Narkdilok, S. (2020). The study of incident rate with relapse use of methamphetamine at Princess Mother National Institute on Drug Abuse Treatment (PMNIDAT). Thai Journal of Addiction, 6(1), 47-58. http://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/pmnidat/article/view/248483
Nilaban, S., Sriherun, B., & Kongthong, U. (2016). Causal relationship of factors affect relapsing behavior of methamphetamine users. Journal of Graduate Studies Valaya Alongkron Rajabhat University, 10(1), 193 - 207. http://So02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JournalGradVRU /article/view/55960
Panya, S. (2017). Study on the risk factors for repeated drug addiction among drug addiction patient at a drug addiction rehabilitation center in the northeast. In Ubonratchatani university. The 2st National Conference Ubon Ratchathani: 4.0 Research for the development of the country towards stability, prosperity and sustainability. (pp. 161-169). Ubonratchatani university.
Panya, S., Thajang, S., Chapik, N., Kanchanabut, S., & Mongkolsawad, J. (2021). The relationship between personal factors, psychosocial factors, and environmental factors among repeated methamphetamine recurrence in Thanyarak hospital. Nursing Journal, 48(2), 273 - 282. http://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/cmunursing/article/view/247286
Phurahong, G. (2018). Factors affecting the relapsing of drug addicted patients in Pathumthani province. Journal of Public health nursing, 32(2), 23 - 40. http://So01.tci-thaijo.org/index. php/phn/article/view/245417
Princess Mother National Institute on Drug Abuse Treatment. (2023). Statistics on patients receiving treatment. Author.
Sirinual, S., Suphunnakul, P., Noosorn, N., & Wongsawad, P. (2016). Factors affecting amphetamine relapse among drug addicts after treatment. Journal of health science research, 10(1), 39 - 45. http://So02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JHR/article/view/68832
Siriwannabut, S. (2020). developmental psychology theory (3rd ed.). CUprint.
The Joanna Briggs Institude. (2014, May 16). Critical appraisal tools. http://joannabriggs.org/ research/ critical-appraisal-tools.htm
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. (2023). Global Overview: Drug Demand Drug Supply. Author.
Valentino, R.J., & Volkow, N.D. (2020). Drugs, sleep, and the addicted brain. Neuropsychophar macology, 45(1), 3 – 5 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0465-x
Zeng, X., Lu, M., & Chen, M. (2021). The relationship between family intimacy and relapse tendency among people who use drugs: A moderated mediation model. Substance Abuse Treatment, Prevention, and Policy, 16(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13011-021-00386-7
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



