Anti-neuroinflammatory activity of Etlingera pavieana rhizomal extract in LPS-induced microglial cells
Keywords:
Anti-inflammatory activity, Etlingera pavieana, Microglial cell, Nitric oxide, Prostaglandins E2Abstract
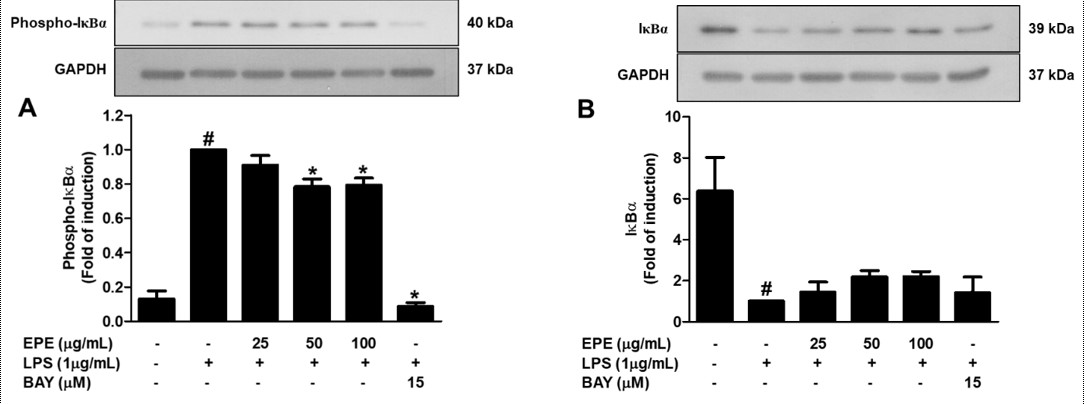
Etlingera pavieana (Pierre ex Gagnep) R.M. Sm., a plant in family Zingiberaceae, has long been used as a spice and a traditional medicine in the East of Thailand. Previous studies have shown that E. pavieana rhizomes inhibited inflammatory response in mouse macrophage cells and human endothelial cells. However, the anti-inflammatory activity of E. pavieana rhizome in microglial cells is yet to be demonstrated. Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of ethanol extract from E. pavieana rhizomes (EPE) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced BV2 microglial cells. Anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated by measurement of the production of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-catalyzed nitric oxide (NO) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-catalyzed prostaglandins E2 (PGE2). Cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay. The level of inflammation-responsive protein and mRNA was investigated by Western blot analysis and qRT-PCR, respectively. EPE at non-cytotoxic concentrations (25 to 100 µg/mL) reduced NO and PGE2 production in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, EPE significantly inhibited the expression of iNOS and COX-2 at protein and mRNA levels. In addition, EPE suppressed the phosphorylation of inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Taken together, our results indicate that EPE exhibits the anti-inflammatory effect in microglial cells in part by inhibiting of the production of NO and PGE2 as well as the expression of iNOS and COX-2 via suppressing nuclear factor-κB activation. The ethanol extract from the E. pavieana rhizome has the potential to be used as a functional food ingredient and dietary supplements for preventing neuroinflammation-related diseases.
References
DiSabato DJ, Quan N, Godbout JP. Neuroinflammation: the devil is in the details. J Neurochem. 2016; 139:136-153.
Milatovic D, Zaja-Milatovic S, Breyer RM, Aschner M, Montine TJ. Neuroinflammation and oxidative injury in developmental neurotoxicity. In: Gupta RC, editor. Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology. 1st ed. Academic Press; 2017. p. 1051-1061.
Smith JA, Das A, Ray SK, Banik NL. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull. 2012;87(1):10-20.
Lull ME, Block ML. Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics. 2010;7(4):354-365.
Voet S, Prinz M, van Loo G. Microglia in central nervous system inflammation and multiple sclerosis pathology. Trends Mol Med. 2018;25(2):112-123.
Gao HM, Hong JS. Why neurodegenerative diseases are progressive: uncontrolled inflammation drives disease progression. Trends Immunol. 2008; 29(8):357-365.
Förstermann U, Sessa WC. Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J. 2011;33(7):829-837.
Dagdeviren M. Role of nitric oxide synthase in normal brain function and pathophysiology of neural diseases. In: Saravi SSS, editor. Nitric Oxide Synthase: Simple Enzyme-Complex Roles. 1st ed. Croatia: IntechOpen; 2017. p. 37-52.
Hein AM, O'Banion MK. Neuroinflammation and memory: the role of prostaglandins. Mol Neurobiol. 2009;40(1):15-32.
Lima IV, Bastos LF, Limborço-Filho M, Fiebich BL, de Oliveira AC. Role of prostaglandins in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:946813.
Sun SC. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(9):545-558.
Dresselhaus EC, Meffert MK. Cellular specificity of NF-κB function in the nervous system. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:1043.
Poulsen AD, Phonsena P. Morphological variation and distribution of the useful ginger Etlingera pavieana (Zingiberaceae). Nord. J. Bot. 2017;35(4):467-475.
Srisook E, Palachot M, Mankhong S, Srisook K. Anti-inflammatory effect of Etlingera pavieana (Pierre ex Gagnep.) RM Sm. rhizomal extract and its phenolic compounds in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017; pp. S230–S235.
Srisook K, Potiprasart K, Sarapusit S, Park CS, Srisook E. Etlingera pavieana extract attenuates TNF-α induced vascular adhesion molecule expression in human endothelial cells through NF-κB and Akt/JNK pathways. Inflammopharmacol. 2020; 28:1649-1662.
Srisook K, Udompong S, Sawai P, Thongyen T. Etlingera pavieana rhizome extract decreases oxidative stress and activates eNOS activity via stimulation of Akt phosphorylation in human endothelial cells. Naresuan Phayao Journal. 2018;11:23-28.
Srisook K, Srisook E, Nachaiyo W, Chan-In M, Thongbai J, Wongyoo K, et al. Bioassay-guided isolation and mechanistic action of anti-inflammatory agents from Clerodendrum inerme leaves. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015; 165:94-102.
Kiaei M. New hopes and challenges for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: great opportunities for young neuroscientists. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2013;4(1):3-4.
Ali TB, Schleret TR, Reilly BM, Chen WY, Abagyan R. Adverse Effects of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Dementia, According to the Pharmacovigilance Databases of the United-States and Canada. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144337.
Brown GC, Neher JJ. Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons. Mol Neurobiol. 2010; 41(2-3):242-247.
Mattson MP, Camandola S. NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J Clin Invest. 2001;107(3):247-254.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Naresuan Phayao Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยาไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย
The authors are themselves responsible for their contents. Signed articles may not always reflect the opinion of University of Phayao. The articles can be reproduced and reprinted, provided that permission is given by the authors and acknowledgement must be given.







