Shelf life extension of ready to eat fish burger using gamma irradiation
Keywords:
Fish burger , Ready to eat, Gamma irradiation, Shelf lifeAbstract
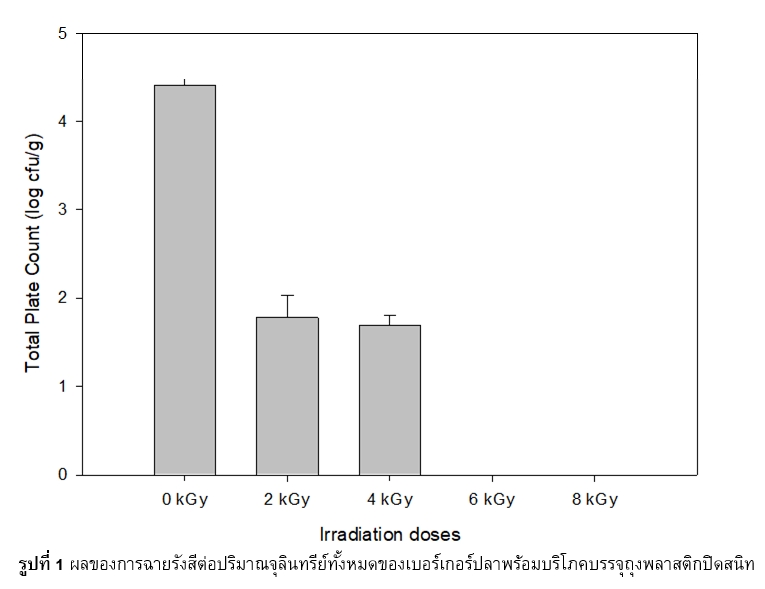
This research aims to extend the shelf life of ready-to-eat (RTE) fish burger. RTE fish burger was prepared from minced salmon (red flesh fish) and minced dory (white flesh fish) at ratio of 50:50, packed in sealed plastic bags and exposed to gamma irradiation at 2, 4, 6 and 8 kGy. Aw and water holding capacity slightly decreased, whereas pH increased after irradiation (p£ 0.05). Distance at failure (fracturability), redness (a*) of burger crust, redness (a*) of burger flesh decreased at 8, 2 and 4 kGy respectively (p£ 0.05). However, panelists accepted irradiated RTE fish burger even at 8 kGy. The RTE fish burger was free from the pathogens including Salmonella spp.,Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus aureus, Clostridium perfringens and Escherichia coli but microbial populations of 4 log CFU/g still remained in the burger. Thus RTE fish burger was spoiled at 3 days of ambient storage (25±5 oC). Gamma irradiation at 8 kGy could destroy entire microbial and extend shelf life of RTE fish burger from 3 days to 2 months at ambient temperature (25±5 oC).
References
Gokoglu N, Yerlikaya P, editors. Seafood Chilling, Refrigeration and Freezing: Science and Technology, 1st ed. Oxford: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; 2015. 248 p.
Chaiyawat M. Spoilage and Analytical Method. In: Department of Fishery Products (Ed.), Science and Technology of Fishery Products. Bangkok: Kasetsart University Press; 2015. 385 p.
Reher D S, Musherraf S, Trimboli S, Caporaso F, Foley D, Prakash A. Irradiation of a prepared meal packed in a modified atmosphere container, 2000 IFT Annual Meeting, Paper 86H-6.
Foley D M, Reher E, Caporaso F, Trimboli S, Musherraf Z., Prakash A. Elimination of Listeria monocytogenes and changes in physical and sensory qualities of prepared meal following gamma irradiation. Food Microbiol. 2001: 18(2): 193-204.
Clardy S, Foley D M, Caporaso F, Calicchia M L, Prakash A. Effect of gamma irradiation on Listeria monocytogenes in frozen, artificially contaminated sandwiches. J. Food Prot. 2002: 65 (11): 1740-1744.
Lamb J L, Gogley J M, Thomson M J, Solis D R, Sen S. Research note: Effect of low-dose gamma irradiation on Staphylococcus aureus and product packaging in ready-to-eat ham and cheese sandwiches. J. Food Prot. 2002: 65(11): 800-1805.
Sommers C, Boyd G. Elimination of Listeria monocytogenes from ready-to-eat turkey and cheese tortilla wraps using ionizing radiation. J. Food Prot. 2005: 68(1): 164-167.
Jo C, Lee N Y, Kang H J, Hong S P, Kim Y H, Kim J K, et al. Inactivation of pathogens inoculated into prepared seafood products for manufacturing Kimbab, steamed rice rolled in dried seaweed by gamma irradiation. J. Food Prot. 2005: 68(2): 396-402.
Yildirim I, Uzunlu S, Topuz A. Effect of gamma irradiation on some principle microbiological and chemical quality parameters of raw Turkish meat ball. Food Control 2005: 16(4): 363-367.
Irawati Z, Natalia L, Nurcahya C M, Anas F. The role of medium radiation dose on microbiological safety and shelf-life of some traditional soups. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2007: 76(11-12): 1847-1854.
Yoon Y M, Park J H, Lee J H, Park J N, Park J K, Sung N Y, et al. Effects of gamma-irradiation before and after cooking on bacterial population and sensorial quality of Dakgalbi. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012: 81(8): 1121-1124.
Kang S, Park S Y, Ha S D. Application of gamma irradiation for the reduction of norovirus in traditional Korean half-dried seafood products during storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016: 65(1): 739-745.
Song H P, Kim B, Jung S, Choe J H, Yun H, Kim Y J, Jo C. Effect of gamma and electron beam irradiation on the survival of pathogens inoculated into salted, seasoned, and fermented oyster. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2009: 42(8): 1320-1324.
Kanatt S R, Chawla S P, Chander R, Sharma A. Development of shelf-stable, ready-to-eat (RTE) shrimps (Penaeus indicus) using -radiation as one of the hurdles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006: 39(6): 621-626.
Ali H A, Mansour E H, El-Fath A, El-Bedawey A, Osheba A S. Evaluation of tilapia fish burgers as affected by different replacement levels of mashed pumpkin or mashed potato. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019: 18(2): 127-132.
Urbain W M, editor. Food Irradiation, 1st ed. Florida: Academic Press, Inc.; 1986. 368 p.
Dvorak P, Kratochv B, Grolichov M. Changes of colour and pH in fish musculature after ionizing radiation exposure. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005: 220(3): 309-311.
Sirisoontaralak P, Suthirak P, Papaka K, Vongsawasdi P. Development of shelf stable chiffon cake using gamma irradiation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017: 75(1): 78-84.
Farkas J. Irradiation for better foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006: 17(4): 148-152.
Thai Industrial Standard Institute. Thai Community Product Standard for Fish Sausages (TCPS No. 143/2555). Bangkok: Ministry of Industry;2012. 7 p.
Chen Q, Cao M, Chen H, Gao P, Fu Y, Liu M, et al. Effects of gamma irradiation on microbial safety and quality of stir fry chicken dices with hot chili during storage. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016: 127(10): 122-126.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Naresuan Phayao Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยาไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย
The authors are themselves responsible for their contents. Signed articles may not always reflect the opinion of University of Phayao. The articles can be reproduced and reprinted, provided that permission is given by the authors and acknowledgement must be given.







