ผลของโปรแกรมส่งเสริมการมีส่วนร่วมของครอบครัวในการดูแลผู้สูงอายุมุสลิม โรคกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือดต่อการรับประทานยาอย่างต่อเนื่อง: การศึกษานำร่อง
คำสำคัญ:
โปรแกรมส่งเสริมการมีส่วนร่วมของครอบครัว, พฤติกรรมการรับประทานยา, ผู้สูงอายุมุสลิม, โรคกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือดบทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์ เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมส่งเสริมการมีส่วนร่วมของครอบครัว
ในการดูแลผู้สูงอายุมุสลิมโรคกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือดต่อการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการรับประทานยาอย่างต่อเนื่อง วิธีการศึกษา เป็นการศึกษานำร่อง กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นผู้สูงอายุมุสลิมโรคกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือดและผู้ดูแล จำนวน 12 ราย (6 คู่) คัดเลือกกลุ่มตัวอย่างตามคุณสมบัติที่กำหนด และได้รับการดูแลตามโปรแกรมฯ เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล โดยใช้แบบสอบถามพฤติกรรมการใช้ยาสำหรับผู้ป่วยที่เป็นโรคหลอดเลือดหัวใจ และแบบประเมินการมีส่วนร่วมของสมาชิกในครอบครัว เครื่องมือทั้งหมดได้ผ่านการประเมินความตรงเชิงเนื้อหา จากผู้ทรงคุณวุฒิจำนวน 3 ท่าน มีค่าความเที่ยงโดยหาค่าสัมประสิทธิ์แอลฟาของครอนบาคได้ 0.95 และ 0.93 ตามลำดับ ทดสอบความเที่ยงโดยนำไปทดลองใช้กับกลุ่มตัวอย่างที่มีลักษณะคล้ายคลึงกับกลุ่มตัวอย่างที่ทำการศึกษาจำนวน 20 ราย วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลโดยใช้สถิติบรรยาย ได้แก่ การแจกแจงความถี่ ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ค่าเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน ส่วนการทดสอบสมมติฐานการวิจัยใช้สถิติวิลคอกซัน
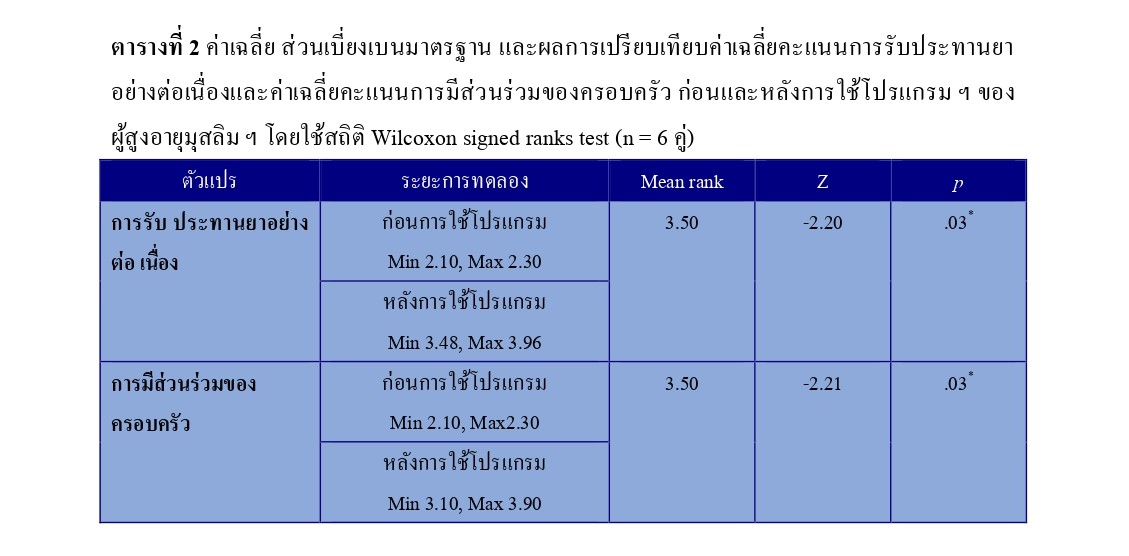
ผลการวิจัย พบว่า ค่าเฉลี่ยคะแนนการรับประทานยาอย่างต่อเนื่องและค่าเฉลี่ยคะแนนการมีส่วนร่วมของครอบครัวของผู้สูงอายุมุสลิมฯ หลังได้รับโปรแกรมสูงกว่าก่อนได้รับโปรแกรมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (Z = -2.20, - 2.21, p < .05)
ผลการศึกษาชี้ให้เห็นว่า โปรแกรมส่งเสริมการมีส่วนร่วมของครอบครัวสามารถส่งเสริมดูแลผู้สูงอายุมุสลิมโรคกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือดให้มีพฤติกรรมการรับประทานยาอย่างต่อเนื่อง โดยอาศัยผู้ดูแลในครอบครัวมีส่วนร่วมในการดูแล ซึ่งสามารถทำให้เกิดความต่อเนื่องได้ในระยะยาวและควรมีการทดสอบประสิทธิภาพของโปรแกรมกับพฤติกรรมสุขภาพอื่น ๆ ในกลุ่มที่นอกเหนือไปจากผู้ป่วยโรคกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือด
เอกสารอ้างอิง
American Heart Association. (2019). Heart disease and stroke statistics A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 139 (10), e56 - e528. http://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.000000 0000001123
Bunchaisuriya, D. (2011). Program development according to Model of the process of changing behavior Food consumption for Thai Muslim patients with High blood pressure [Master’s thesis]. Prince of Songkla University.
Dai, X., Hummel, S.L., Salazar, J.B., Taffet, G.E., Zieman, S., & Schwartz, J.B. (2015). Cardiovascular physiology in the older adults. Journal of Geriatric Cardiology, 12(3), 196 - 201. http://doi.org/10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2015.03.015
Department of Disease Control. (2019, March 15). Number and death rate of non-communicable diseases, 2016 – 2018. http://www.thaincd.com /2016 /mission/documents-detail.php?id= 13653&tid=32&gid=1-020
Department of Disease Control. (2020, March 15). Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) situation 2019. https://ddc.moph.go.th
Kanbuala, W., Aiadsuy, N., & Deenan, A. (2021). The Effects of a Health Literacy Promotion Program on Coronary Artery Disease Preventive Behaviors and Serum Lipid Levels Among People with Dyslipidemia. Journal of Faculty of Nursing Burapha University, 29(3), 186 - 195. https://ojs.lib.buu.ac.th/index.php/nursing/article/view/7683
Lillahkul, N., & supanakul, P. (2018). Way of Life of Muslim People in Thailand’s Southern Provinces and Health Promoting Lifestyle. The Southern College Network Journal of Nursing and Public Health, 5(2), 302 - 312. https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/scnet/article /view/130912
Lutfi, I. (2013). Muslim life principles (4th ed.). Friendship Printing House.
Pattani Provincial Public Health. (2019, January 17). Chronic Disease Patient Statistics Pattani Province. http://www.chronic.sasukpattani.com
Penpimol, P., Charoenkitkarn, V., Wattanakitkrileart, D., & Dumavibhat, C. (2016). The Influence of Perceived Medication Necessity, Medication Concern, Patient-Healthcare Provider Communication, and Complexity of Medical Regimens on Medication Adherence in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome after Hospitalization. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses. 17(3), 149 - 157. https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JRTAN/article/view/73275
Samae, P., Komjakraphan, P., & Piriyakunthorn, S. (2016). Development of an Oral Medication Self-Management Handbook for Elderly Muslim Patients with Diabetes. Songklanagarind Journal of Nursing, 36(2), 171 - 180. https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/nur-psu/article/view/65348
Supanam, S., Liangchawengwong, S., & Piyayotai, D. (2020). The factors predicting post-hospital discharge chest pain status among acute coronary syndrome patients during the first year. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 21(1), 283 - 292. https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index. php/JRTAN/article/view/241572
Suwannapong, K., Thanasilp, S., & Chaiyawat, W. (2016). The Development of Medication Adherence Scale for Persons with Coronary Artery Diseases: a Delphi study. Journal of Health Research, 30(3), 149 - 154. https://www.thaiscience.info/journals/Article/JHRE /10981369.pdf
Suwannapong, K., Thanasilp, S., & Chaiyawat, W. (2019). The Development of Medication Adherence Scale for Persons with Coronary Artery Disease (MAS-CAD): A Nursing Perspective. Walailak Journal of Science & Technology 16(1), 19 - 25. https://wjst.wu.ac.th/ index.php/wjst/article/view/4046
Thai Health Stat. (2020, November). Coronary and artery disease. https://www.hiso.or.ththai healthstat/area/index.php?ma=1&pf=01818101&tm=2&tp=3303
Wangji, N., Boonyasopun, U., & Sikeaw, M. (2015). Effect of Behavioral Modification program on Medical Adherence and Blood pressure for Muslim Elderly with Uncontrolled Hypertention. In Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, The national Graduate Research Conference (34th ed.). Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University.
World Health Organization. (2010, December 14). Treatment of Tuberculosis Guidelines. https://www.aidsdatahub.org/sites/default/files/resource/treatment-tuberculosis-guidelines-fourth-edition.pdf
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารมหาวิทยาลัยนราธิวาสราชนครินทร์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



