การตรวจสอบคุณสมบัติแบคทีเรียกรดแล็กติกเพื่อเป็นโพรไบโอติกส์สำหรับหมักเครื่องดื่มแพลนต์เบสต์
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
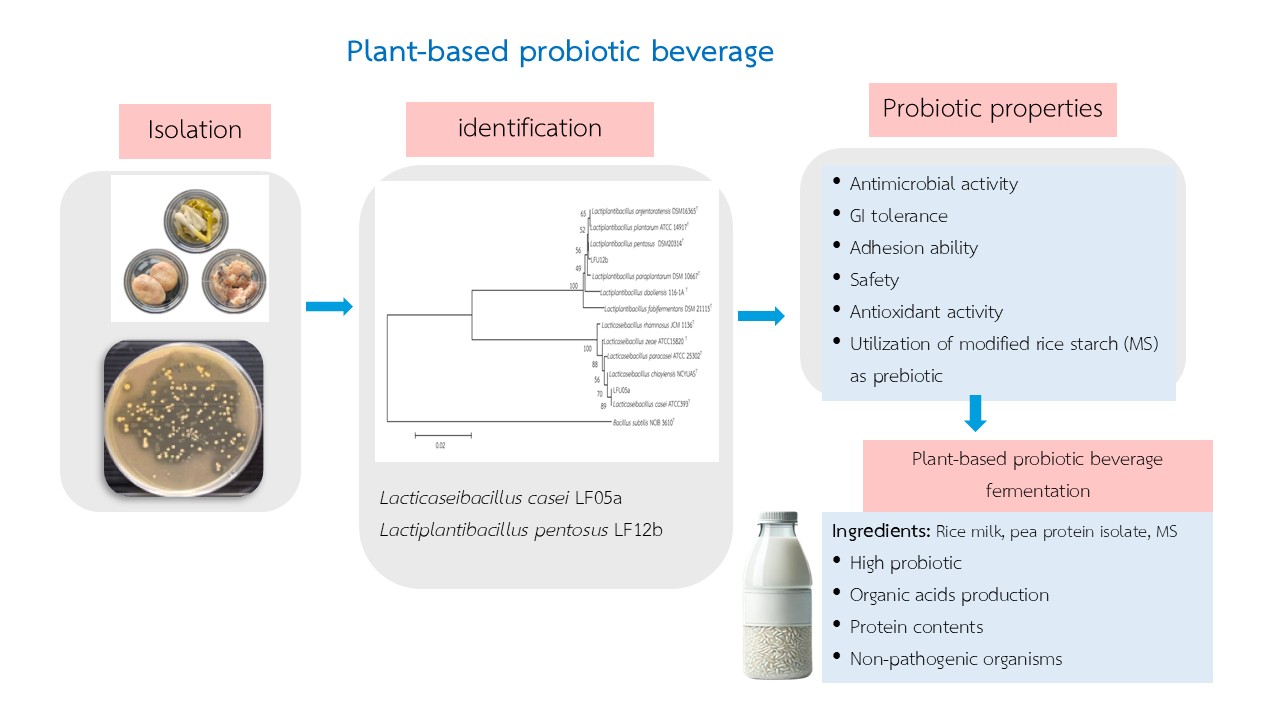
ผลิตภัณฑ์โพรไบโอติกส์แพลนต์เบสต์เป็นอาหารเพื่อสุขภาพประเภทหนึ่ง วัตถุประสงค์์ของการศึกษานี้เพื่อคัดเลือกแบคทีเรียกรดแล็กติกและประเมินคุณสมบัติการเป็นโพรไบโอติกส์เพื่อใช้เป็นหัวเชื้อในการผลิตเครื่องดื่มหมักแพลนต์เบสต์ ไอโซเลต LFU05a และ LFU12b ถูกเลือกไปศึกษาต่อเนื่องจากมีประสิทธิภาพในการยับยั้งแบคทีเรียก่อโรคทดสอบได้สูง สามารถรอดชีวิตเมื่อทดสอบภายใต้สภาวะจำลองของทางเดินอาหาร (ร้อยละ 67.54-73.83) มีคุณสมบัติในการเกาะที่ดี ไม่ย่อยสลายเม็ดเลือดแดง มีความไวต่อยาปฏิชีวนะและมีกิจกรรมต้านอนุมูลอิสระ (ร้อยละ 64.23-83.26) ไอโซเลต LFU05a และ LFU12b ถูกจำแนกว่าตรงกับเชื้อ Lacticaseibacillus casei และ Lactiplantibacillus pentosus ตามลำดับ สำหรับการคัดเลือกพรีไบโอติกส์พบว่าแป้งข้าวดัดแปลงมีสมบัติในการเป็นพรีไบโอติกส์สำหรับการส่งเสริมการเจริญของโพรไบโอติกส์สายพันธุ์ LFU05a และ LFU12b ทั้งนี้เครื่องดื่มหมักแพลนต์เบสต์จากข้าวเสริมโปรตีนสกัดจากถั่วลันเตาร้อยละ 10 และแป้งข้าวดัดแปลงร้อยละ 1 มีเชื้อโพรไบโอติกส์ปริมาณสูง (8.45 log CFU/ml) ผลการทดลองนี้บ่งชี้ว่า L. casei LFU05a และ L. pentosus LFU12b เป็นหัวเชื้อที่มีศักยภาพในการผลิตเครื่องดื่มหมักแพลนต์เบสต์โพรไบโอติกส์
Article Details
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Dudek-Wicher, R., Junka, A., Paleczny, J. and Bartoszewicz, M., 2020, Clinical trials of probiotic strains in selected disease entities, Int. J. Microbiol. 2020: 8854119.
Ghosh, T., Beniwal, A., Semwal, A. and Navani, N.K., 2019, Mechanistic insights into probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria associated with ethnic fermented dairy products, Front. Microbiol. 10: 502.
Deng, Z., Hou, K., Zhao, J. and Wang, H., 2021, The probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria and their applications in animal husbandry, Curr. Microbiol. 79(1): 22.
Shen, F., Zhuang, J., Wang, Q., Zhang, J., Liu, T., Ruan, S., Du, J., Zhong, H., Zhao, M. and Feng, F., 2023, Screening of novel probiotics with intestinal peristalsis - promoting potential based on in vitro and in vivo investigations, Food Bios. 53:102681.
Gebre, T.S., Emire, S.A., Chelliah, R., Aloo, S.O. and Oh,D., 2023, Isolation, functional activity, and safety of probiotics from Ethiopian traditional cereal-based fermented beverage,“Borde”, LWT.184:115076.
Gibson, G.R., Hutkins, R., Sanders, M.E., Prescott, S.L., Reimer, R.A., Salminen, S.J., Scott, K., Stanton, C., Swanson, K.S., Cani, P.D., Verbeke, K. and Reid, G., 2017, Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics, Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14:491-502.
Ashwar, B.A., Gani, A., Ashraf, Z., Jhan, F., Shah, A., Gani, A. and Wani, T.A., 2021, Prebiotic potential and characterization of resistant starch developed from four Himalayan rice cultivars using β -amylase and transglucosidase enzymes, LWT. 143:111085.
Meidong, R., Seangkaew, B., Thammaporn, R. and Thipsing, S., 2023, Effect of modified ice starch on enhancing survival of probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BL60a in synbiotic gummy candy supplemented with khao-mak, Thai Sci. Technol. J. 31(3): 105-118 (in Thai).
Verduci, E., D'Elios, S., Cerrato, L., Comberiati, P., Calvani, M., Palazzo, S., Martelli, A., Landi, M., Trikamjee, T. and Peroni, D.G., 2019, Cow's milk substitutes for children: nutritional aspects of milk from different mammalian species, special formula and plant-based beverages, Nutrients. 11(8): 1739.
Escobar-Sáez, D., Montero-Jiménez, L., García-Herrera, P. and Sánchez-Mata, M.C., 2022, Plant-based drinks for vegetarian or vegan toddlers: nutritional evaluation of commercial products, and review of health benefits and potential concerns, Food Res. Int. 160:111646.
Haas, R., Schnepps, A., Pichler, A. and Meixner, O., 2019, Cow milk versus plant - based milk substitutes: a comparison of product image and motivational structure of consumption, Sustainability. 11(8):5046.
Verma, D.K. and Srivastav, P.P., 2020, Bioactive compounds of rice (Oryza sativa L.): Review on paradigm and its potential benefit in human health, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 97: 355-365.
Wu, D. T., Li, W. X., Wan, J. J., Hu, Y. C., Gan, R . Y . and Zou, L., 2023, Comprehensive review of pea (Pisum sativum L.): chemical composition, processing, health benefits, and food applications, Foods. 12(13): 2527.
Meidong, R., Khotchanalekha, K., Doolgindachbaporn, S., Nagasawa, T., Nakao, M., Sakai, K. and Tongpim, S., 2018, Evaluation of probiotic Bacillus aerius B81e isolated from healthy hybrid catfish on growth, disease resistance and innate immunityofPla-mong Pangasius bocourti, Fish Shellfish Immunol. 73: 1-10.
Huang, Y. and Adams, M.C., 2004, In vitro assessment of the upper gastrointestinal tolerance of potential probiotic dairy propionibacteria, Int. J. Food Microbiol. 91(3):253-260.
Tallon, R., Arias, S., Bressollier, P. and Urdaci, M.C., 2007, Strain- and matrix - dependent adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum is mediated by proteinaceous bacterial compounds, J. Appl. Microbiol. 102(2): 442-451.
Selvin, J., Maity, D., Sajayan, A. and Kiran, G.S., 2020, Revealing antibiotic resistance in therapeutic and dietary probiotic supplements, J. Glob. Antimicrob.Resist. 22: 202-205.
Jang, H.J., Song, M.W., Lee, N.K. and Paik, H.D., 2018, Antioxidant effects of live and heat-killed probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Ln1 isolated from kimchi, J. Food Sci. Technol. 55(8): 3174-3180.
Safronova, L.S., Skorochod, I.A. and Ilyash, V.M., 2021, Antioxidant and antiradical properties of probiotic strains Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ssp. plantarum, Probiotics Antimicro. Prot.13:1585-1597.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G. and Kumar, S., 2021, MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11, Mol. Biol. Evol. 38(7): 3022-3027.
Wang, S., Chelikani, V. and Serventi, L., 2018, Evaluation of chickpea as alternative to soy in plant-based beverages, fresh and fermented, LWT. 97: 570-572.
Mazlumi, A., Panahi, B., Hejazi, M.A. and Nami, Y., 2022, Probiotic potential characterization and clustering using unsupervised algorithms of lactic acid bacteria from saltwater fish samples, Sci. Rep. 12: 11952.
EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards, 2017, Scientific opinion on the maintenance of the list of QPS biological agents intentionally added to food and feed, EFSA J. 15(3): e04664.
Jang, W. J., Kim, C. E., Jeon, M., Lee, S., Lee, J. M., Lee, E. and Hasan, T., 2021, Characterization of Pediococcus acidilactici FS2 isolated from Korean traditional fermented seafood and its blood cholesterol reduction effect in mice, J. Funct. Foods. 87: 104847.
Dinev,T., Rusenova, N., Velichkova, K. and Beev, G., 2022, Antimicrobial potential of eleven Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strains isolated from mountain anthills, Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 28: 949-955.
Nishiyama, K., Takaki, T., Sugiyama, M., Fukuda, I., Aiso, M., Mukai, T., Odamaki, T., Xiao, J. Z., Osawa, R. and Okada, N., 2020, Extracellular vesicles produced by bifidobacterium longum export mucin - binding proteins, Appl.Environ. Microbiol. 86(19): e01464-20.
Hoffmann, A., Kleniewska, P. and Pawliczak, R., 2019, Antioxidative activity of probiotics, Arch. Med. Sci. 17(3): 792-804.
Zheng, Y., Wang, Q., Li, B., Lin, L.,Tundis, R., Loizzo, M. R., Zheng, B. and Xiao, J., 2016, Characterization and prebiotic effect of the resistant starch from purple sweet potato, Molecules. 21(7): 932.
Arshad, N. H., Zaman,S. A., Rawi, M.H. and Sarbini, S. R., 2018, Resistant starch evaluation and in vitro fermentation of Lemantak (native sago starch), for prebiotic assessment, Int. Food Res. J. 25(3): 951-957.
Ja iturong, P., Laosirisathian, N., irithunyalug, B., Eitssayeam, S., Sirilun, S., Chaiyana, W. and Sirithunyalug, J., 2020, Physicochemical and prebiotic properties of resistant starch from Musa sapientum Linn., ABB group, cv. Kluai Namwa Luang, Heliyon. 6(12): e05789.
Hettige, K.D.T., Jayarathna, G.E.D.A.M. and Wijewardane, R.M.N.A., 2020, Prebiotic potential of resistant starchesand dietary fibers of Sri Lankan traditional rice varieties and its application in the food industry, J. Dry Zone Agr. 6(2): 60-67.
Rathore, S., Salmerón, I. and Pandiella, S.S., 2012, Production of potentially probiotic beverages using single and mixed cereal substrates fermented with lactic acid bacteria cultures, Food Microbiol. 30: 239-244.