The comparison of phenolic compounds, flavonoids and antioxidant activities of the ethanolic extracts of shoots, leaves, fruits and seeds of Leucaena leucocephala
Keywords:
Leucaena leucocephala, antioxidant activities, phenolic compounds, flavonoidsAbstract
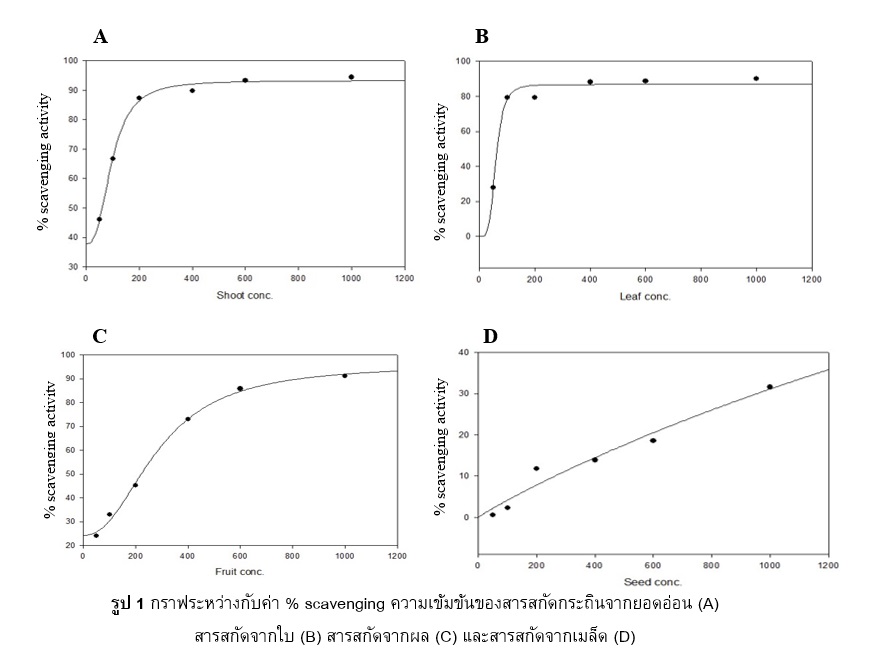
Leucaena leucocephala is a very common plant in Thailand, which is herbal eaten together with traditional food. This study aimed to compare phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and antioxidant activities of the ethanolic extracts of shoots, leaves, fruits, and seeds of Leucaena leucocephala. Crude ethanolic extracts were prepared by maceration and rotary evaporation. There were 3 experiments including, phenolic compounds analysis by using Folin-Ciocalteu Colorimetric method, flavonoids analysis by aluminum chloride colorimetric method, and the antioxidant activity was using DPPH radical scavenging assay. In phenolic compounds analysis, the result showed that the ethanolic extract from shoots had the highest amount of phenolic compounds. There was 1,660.79±93.71 mg gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram of extract, followed by leaves, fruits, and seeds, respectively. Flavonoids analysis, the result showed that the leaves extract had the highest amount of flavonoids, there was 518.83±18.76 mg quercetin equivalent (QE) per gram of extract, followed by shoots, fruits, and seeds, respectively. DPPH radical scavenging assay, the result showed that the leaves extract had the highest antioxidant activity that SC50 value 59.39 μg/mL, followed by shoots, fruits, and seeds, respectively. This study can conclude that the leaves extract had the highest antioxidant activity in comparison with other parts of Leucaena leucocephala that related to the amount of flavonoids.
References
Pham-Huy LA, He H, Pham-Huy C. Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. Int J Biomed Res. 2008;4(2):89-96.
Dzoyem JP, Eloff JN. Anti-inflammatory, anticholinesterase and antioxidant activity of leaf extracts of twelve plants used traditionally to alleviate pain and inflammation in South Africa. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;160:194-201.
Zayed MZ, Sallam SMA, Shetta ND. Review article on leucaena leucocephala as one of the miracle timber trees. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2017;10(1):1-7.
Soottawat Benjakul, Phanat Kittiphattanabawon, Punnanee Sumpavapol, Sajid Maqsood. Antioxidant activities of lead (Leucaena leucocephala) seed as affected by extraction solvent, prior dechlorophyllisation and drying methods. J Food Sci Technol. 2014;51(11):3026-3037.
Ratikorn Chatchanayuenyong, Patcharawan Sujayanont, Auranut Vuttivirojana. Effects of Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) de Wit Leaves Extracts in Culture of Human Umbilical Vein Cells. Pharmacogn J. 2018;10(1):148-153.
Dewanto V WX, Adom KK, Liu RH. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50(10):3010-3014.
Prommuak C, De-Eknamkul W, Shotipruk A. Extraction of flavonoids and carotenoids from Thai silk waste and antioxidant activity of extracts. Sep Purif Technol. 2008;62(2):444-448.
Singsai K, Akaravichien T, Kukongviriyapan V, Sattayasai J. Protective Effects of Streblus asper Leaf Extract on H2O2-Induced ROS in SK-N-SH Cells and MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Disease-Like Symptoms in C57BL/6 Mouse. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:970354.
Adekunle OK, Akinlua A. Nematicidal effects of Leucaena leucocephala and Giricidia sepium extracts on meloidogyne incognita infecting okra. J Agric Sci. 2007;52(1):53-63.
Chowtivannakula P, Srichaikulb B, Talubmook C. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of seed extract from Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) de Wit. Agric Nat Resour. 2016;50(5):357-361.
Benjakul S, Kittiphattanabawon P, Sumpavapol P, Maqsood S. Antioxidant activities of lead (Leucaena leucocephala) seed as affected by extraction solvent, prior dechlorophyllisation and drying methods. J Food Sci Technol. 2014;51(11):3026–3037.
Laotho S, Sritontip C, Sritontip P. Relationship between chlorophyll content, total phenolic, antioxidant activities and SPAD value of Gymnema inodorum Decne. under different nitrogen fertilizer. Khon Kaen Agr J. 2014;42(3):795-801.
Koodkaew I, Limpichotikul P. Study of Antioxidant Activity and Correlation of Antioxidant Compounds in Eight Species of Garden Herbs. SDU Res J. 2017;10(1):137-152.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Naresuan Phayao Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยาไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย
The authors are themselves responsible for their contents. Signed articles may not always reflect the opinion of University of Phayao. The articles can be reproduced and reprinted, provided that permission is given by the authors and acknowledgement must be given.







