The inhibitory effect of Pogonatherum paniceum extracts on HT29 colorectal cancer cells growth
Keywords:
Colorectal cancer, Anticancer, Apoptosis, Pogonatherum paniceum extractsAbstract
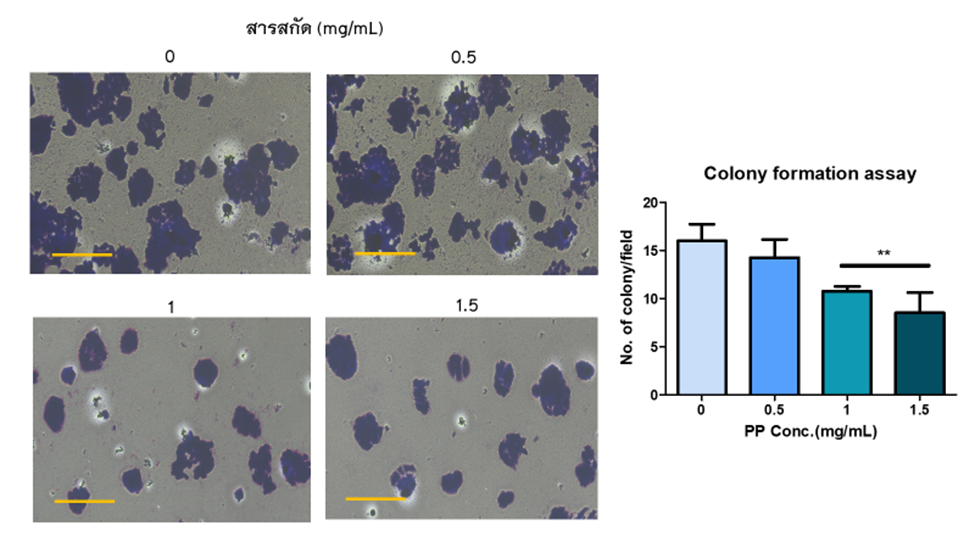
Colorectal cancer is the third most frequent cancer worldwide. It is more common in adults over the age of 50, while environmental and genetic variables have a part to play in etiology. However, studies have indicated that nutrition plays a role in both the cause and prevention of colon cancer. Pogonatherum paniceum (Lam.) Hack (PP) is a grass family with exceptional detoxification properties. This study is focused on the anti-proliferative effect of PP extract and apoptosis related mechanism. MTT, MTS, and colony formation assays were used to evaluate the anti-proliferative activities of human HT29 colon cancer cells. The results suggest that greater concentrations of PP extract reduced the viability of HT29 cancer cells after 48 hours, as shown by an IC50 of 1.2 ± 0.06 mg/mL. Moreover, PP extract induces apoptosis in HT29 cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner (0.5-0.75 mg/mL). In conclusion, PP extract is an alternative treatment for colorectal cancer cells.
References
Chueh AC, Tse JWT, Tögel L, Mariadason JM. Mechanisms of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor-Regulated Gene Expression in Cancer Cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Jul 1;23(1):66–84.
Rs W. Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR [Internet]. 2011 Sep 26 [cited 2023 Mar 29];30(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21943236/
Pavlova NN, Zhu J, Thompson CB. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. 2022 Mar 1;34(3):355–77.
Angwa LM, Jiang Y, Pei J, Sun D. Antioxidant Phytochemicals for the Prevention of Fluoride-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis: a Review. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Mar;200(3):1418–41.
Muniyandi K, George E, Sathyanarayanan S, George BP, Abrahamse H, Thamburaj S, et al. Phenolics, tannins, flavonoids and anthocyanins contents influenced antioxidant and anticancer activities of Rubus fruits from Western Ghats, India. Food Sci Hum Wellness. 2019 Mar;8(1):73–81.
Junsongduang A, Nabundit O, Chinnawong P, Tanming W, Balslev H. Medicinal Plants Used by Tai Lao Healers in Roi Et Thailand. 2021.
Ai T, Liao X, Li R, Fan L, Luo F, Xu Y, et al. GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase from Pogonatherum paniceum enhances salinity and drought tolerance of transgenic tobacco. Z Naturforschung C J Biosci. 2016;71(7–8):243–52.
Kumar P, Nagarajan A, Uchil PD. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018 Jun 1;2018(6).
Wang Y, Nguyen DT, Yang G, Anesi J, Kelly J, Chai Z, et al. A Modified MTS Proliferation Assay for Suspended Cells to Avoid the Interference by Hydralazine and β-Mercaptoethanol. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2021 Apr;19(3):184–90.
Ratsada P, Hijiya N, Hidano S, Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Uchida T, et al. DUSP4 is involved in the enhanced proliferation and survival of DUSP4-overexpressing cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jul 30;528(3):586–93.
Praphasawat R, Thakaew S, Rawangkan A, Thongboontho R, Sooksaen P, Laovittayangkoon S, et al. Anticancer and Antimutagenic Properties of Pogonatherum paniceum on Colorectal Cancer Cells. World J Oncol. 2023 Aug;14(4):266–76.
Bona NP, Pedra NS, Azambuja JH, Soares MSP, Spohr L, Gelsleichter NE, et al. Tannic acid elicits selective antitumoral activity in vitro and inhibits cancer cell growth in a preclinical model of glioblastoma multiforme. Metab Brain Dis. 2020 Feb;35(2):283–93.
Chen KS, Hsiao YC, Kuo DY, Chou MC, Chu SC, Hsieh YS, et al. Tannic acid-induced apoptosis and -enhanced sensitivity to arsenic trioxide in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Leuk Res. 2009 Feb;33(2):297–307.
Darvin P, Baeg SJ, Joung YH, Sp N, Kang DY, Byun HJ, et al. Tannic acid inhibits the Jak2/STAT3 pathway and induces G1/S arrest and mitochondrial apoptosis in YD-38 gingival cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2015 Sep;47(3):1111–20.
Yoshioka K, Kataoka T, Hayashi T, Hasegawa M, Ishi Y, Hibasami H. Induction of apoptosis by gallic acid in human stomach cancer KATO III and colon adenocarcinoma COLO 205 cell lines. Oncol Rep. 2000;7(6):1221–3.
The anthocyanin metabolites gallic acid, 3-O-methylgallic acid, and 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde decrease human colon cancer cell viability by regulating pro-oncogenic signals - PubMed [Internet]. [cited 2023 Mar 31]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23124926/
Subramanian AP, Jaganathan SK, Mandal M, Supriyanto E, Muhamad II. Gallic acid induced apoptotic events in HCT-15 colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 21;22(15):3952–61.
Yuan JM, Sun C, Butler LM. Tea and cancer prevention: epidemiological studies. Pharmacol Res. 2011 Aug;64(2):123–35.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 University of Phayao

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยาไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย
The authors are themselves responsible for their contents. Signed articles may not always reflect the opinion of University of Phayao. The articles can be reproduced and reprinted, provided that permission is given by the authors and acknowledgement must be given.







