การหาสภาวะการสกัดโปรตีนจากถั่วเหลืองด้วยสนามไฟฟ้าแรงสูงแบบจังหวะ
คำสำคัญ:
ถั่วเหลือง, โปรตีน, แรงดันไฟฟ้า, ความสิ้นเปลืองพลังงานจำเพาะ, สมบัติเชิงหน้าที่บทคัดย่อ
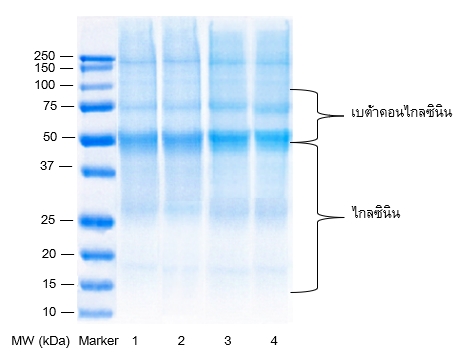
งานวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาหาสภาวะที่ใช้ในการสกัดโปรตีนจากถั่วเหลืองด้วยสนามไฟฟ้าแรงสูงแบบจังหวะ โดยแบ่งการศึกษาออกเป็น 3 ส่วนคือ ในส่วนแรกทำการหาเวลาที่เหมาะสมในการสกัดที่แรงดันไฟฟ้า 10.5 11.5 และ 12.5 กิโลโวลต์ โดยพิจารณาจากเวลาที่มีปริมาณโปรตีน ร้อยละผลผลิตและค่าความเสียหายของเยื่อหุ้มเซลล์สูงที่สุด จากนั้นทำการศึกษาในส่วนที่สองคือ การศึกษาผลของแรงดันไฟฟ้าต่อปริมาณโปรตีน ร้อยละผลผลิตของโปรตีน รูปแบบของโปรตีนและสมบัติเชิงหน้าที่ของโปรตีนรวมทั้งความสิ้นเปลืองพลังงานจำเพาะในการสกัด เพื่อหาแรงดันไฟฟ้าที่เหมาะสมสำหรับการสกัดโปรตีน จากนั้นทำการศึกษาในส่วนสุดท้ายคือ การศึกษาผลของอัตราส่วนของถั่วเหลืองต่อน้ำที่ใช้ในการสกัดต่อปริมาณโปรตีน ร้อยละผลผลิตของโปรตีน รูปแบบของโปรตีนและสมบัติเชิงหน้าที่ของโปรตีนเพื่อหาอัตราส่วนของแข็งต่อตัวทำละลายที่เหมาะสมสำหรับการสกัดโปรตีน โดยผลการศึกษาพบว่า การสกัดโปรตีนจากถั่วเหลืองด้วยสนามไฟฟ้าแรงสูงแบบจังหวะด้วยแรงดันไฟฟ้า 12.5 กิโลโวลต์ เป็นเวลา 60 นาที ในอัตราส่วนถั่วเหลืองต่อน้ำ เท่ากับ 1:15 โดยมวลต่อปริมาตร เป็นสภาวะการสกัดที่เหมาะสม เนื่องจากส่งผลให้มีค่าปริมาณโปรตีน ร้อยละผลผลิตและสมบัติเชิงหน้าที่ของโปรตีนดีที่สุด โดยมีรูปแบบโปรตีนเป็นกลุ่มเบต้าคอนไกลซินิน (7S) ซึ่งเป็นกลุ่มที่ส่งผลต่อสมบัติเชิงหน้าที่มากที่สุด
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Yu X, Gouyo T, Grimi N, Bals O, Vorobiev E. Pulsed electric field pretreatment of rapeseed green biomass (stems) to enhance pressing and extractives recovery. Bioresour Technol. 2016;199:194-201.
Lopez N, Puertolas E, Condon S, Raso J. Enhancement of the extraction of betanine from red beetroot by pulsed electric fields. J Food Eng. 2009;90:60-66.
Ghosh S, Gillis A, Sheviryov J, Levkov K. Towards waste meat biorefinery: Extraction of proteins from waste chicken meat with non-thermal pulsed electric fields and mechanical pressing. J Clean Prod. 2018;208: 220-231.
Loginova K V, Lebovka N I, Vorobiev E. Pulsed electric field assisted aqueous extraction of colorants from red beet. J Food Eng. 2011;106:127-133.
Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72(1-2):248-254.
Yousf N, Nazir F, Salim R, Ahsan H, Sirwal A. Water solubility index and water absorption index of extruded product from rice and carrot blend. J Pharmacog Phytochem. 2017;6(6):2165-2168.
Naowakul B, Wirjantoro T, Phianmongkhol A. Effects of speed and time of wet milling on properties of dietary fiber powder from pomelo's albedo. Food App Biosci J. 2013;1(1):34-48.
Chareemuy W, Tangduangdee C, Viriyarattanasak C. Dehulling effectiveness and properties of full–fat soy flour as affected by thermal treatments. J Agric Sci. 2020;49(1):96–112.
Polikovsky M, Fernand F, Sack M, Frey W, Müller G, Golberg A. Towards marine biorefineries: Selective proteins extractions from marine macroalgae Ulva with pulsed electric fields. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2016;37:194-200.
Goettel M, Eing C, Gusbeth C, Straessner R, Frey W. Pulsed electric field assisted extraction of intracellular valuables from microalgae. Algal Res. 2013;2(4):401-408.
Valle E D, Marracino P, Pakhomova O, Libert M, Apollonio F. Nanosecond pulsed electric signals can affect electrostatic environment of proteins below the threshold of conformational effects: The case study of SOD1 with a molecular simulation study. PLoS One. 2019;14(8):e0221685.
Hosain D, Hosainpour A, Farzad N, Mohammad-Hadi K. Ohmic processing: temperature dependent electrical conductivities of lemon juice. Modern App Sci. 2011;5(1):209-216.
Liu Z, Chang SKC, Li L, Tatsumi E. Effect of selective thermal denaturation of soybean proteins on soymilk viscosity and tofu's physical properties. Food Res Inter. 2004;37(8):815-822.
Redondo D, Venturini M E, Luengo E, Raso J, Arias E. Pulsed electric fields as a green technology for the extraction of bioactive compounds from thinned peach by-products. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2018;45:335-343.
Dehez F, Delemotte L, Kramar P, Miklavcic D, Tarek M. Evidence of conducting hydrophobic nanopores across membranes in response to an electric field. J Physic Chem C. 2014;118(13):6752-6757.
Chindapan R. Food foams. J Food Technol, Siam University. 2005;1(1):12-16.
Rattanapanone N. Basic principles of food processing, 1st ed. Bangkok: Odeon Store; 2001. 148 p.
Xu Y, Wang Z, Qi B, Ran A, Guo Z, Jiang L. Effect of oxidation on quality of Chiba tofu produced by soy isolate protein when subjected to storage. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1877.
He G, Yin Y, Yan X, Wang Y. Application of pulsed electric field for treatment of fish and seafood. In: Miklavcic D, editor. Handbook of electroporation, 1st ed. Zug: Springer International Publishing AG. 2017. p. 2637-2655.
He D, Zhang Z, Li H, Xia Y, Li X, Chen T. Optimizing functional properties of perilla protein isolate using the response surface methodology. Food Sci Technol. 2018;38(2):348-355.
Kanthamoon K, Varith J, Narkprasom K, Tanongkankit Y. Application of pulsed electric field for extraction of soy protein. Proceeding of the 12th International Conference on Science, Technology and Innovation for Sustainable Well-Being (STISW XII); 2020 Jun 26-28; Phetchaburi, Thailand. Silpakorn University; 2020.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 วารสารนเรศวรพะเยา

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย







