พฤติกรรมการไหลของน้ำสลัดไขมันต่ำจากการใช้แป้งข้าวเจ้า ร่วมกับแซนแทนกัมเป็นสารให้ความข้นหนืด
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
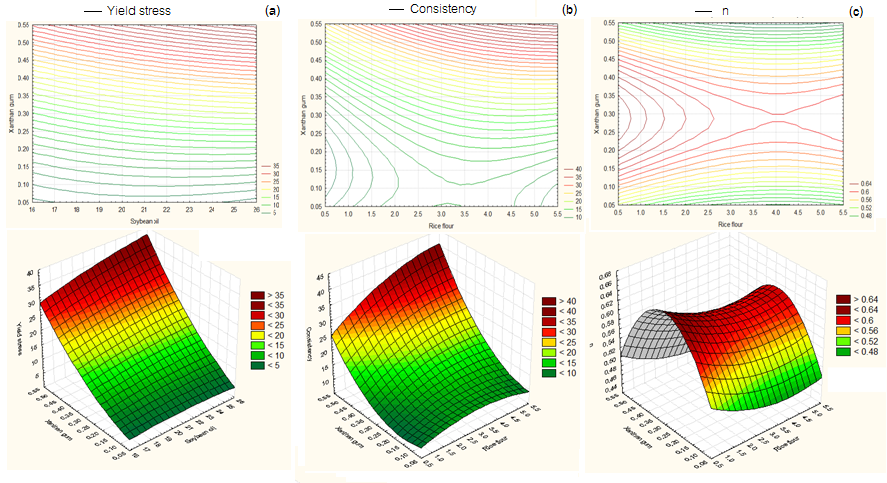
งานวิจัยนี้ศึกษาพฤติกรรมการไหลของน้ำสลัดไขมันต่ำ จากการใช้แป้งข้าวเจ้าร่วมกับแซนแทนกัมเป็นสารให้ความข้นหนืด โดยวางแผนการทดลองแบบ central composite design (CCD) เพื่อศึกษาผลของตัวแปรอิสระ 3 ตัวแปร คือ ปริมาณน้ำมันถั่วเหลือง (x1) ร้อยละ 16.84-25.2 แป้งข้าวเจ้า (x2) ร้อยละ 0.9-5.1 และแซนแทนกัม (x3) ร้อยละ 0.09-0.51 โดยน้ำหนัก ต่อค่าตัวแปรตามที่ได้จากสมการ Herschel-Bulkley ได้แก่ ค่า yield stress (y1), consistency coefficient (K) (y2) และ flow behavior index (n) (y3) พบว่า เมื่อน้ำมันถั่วเหลืองและแซนแทนกัมมากขึ้น ส่งผลให้ค่า yield stress สูงขึ้น เมื่อแป้งข้าวเจ้าและแซนแทนกัมมากขึ้น ส่งผลให้ค่า consistency coefficient สูงขึ้น นอกจากนี้พบว่าค่า flow behavior index มีค่าสูงสุดเท่ากับ 0.64 จาก contour plot เมื่อใช้แป้งข้าวเจ้าร้อยละ 2.65 และแซนแทนกัมร้อยละ 0.28 เมื่อนำน้ำสลัดไขมันต่ำที่มีพฤติกรรมการไหลที่ใกล้เคียงกับน้ำสลัดไขมันต่ำทางการค้าจำนวน 3 สูตร มาทดสอบการยอมรับทางประสาทสัมผัสด้วยวิธี 9-Point Hedonic Scale พบว่า อัตราส่วนของน้ำมันถั่วเหลือง แป้งข้าวเจ้า และแซนแทนกัม ที่ได้รับคะแนนการยอมรับมากที่สุดทางด้านเนื้อสัมผัส ความข้นหนืด สี รสชาติ กลิ่นรส และความชอบโดยรวม คือ 24.04 : 4.5 : 0.45 โดยน้ำหนัก
Article Details
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับมหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆในมหาวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว