Development of sugars quantification method using polarimeter couple with UV-Visible quartz cuvette cell
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.60045/hsstr-2023-256482คำสำคัญ:
Sugars, Polarimetric method, UV-Visible quartz cuvette cell, Sodium chlorideบทคัดย่อ
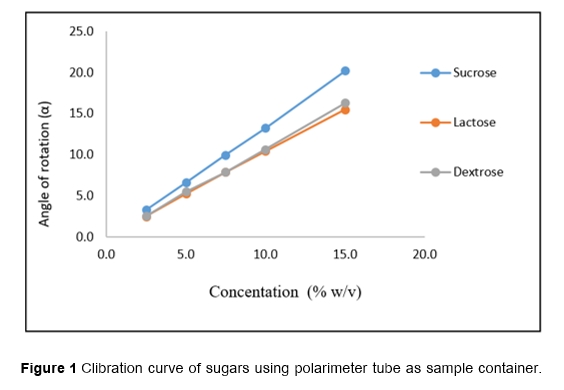
The objective of this study was to develop the method for determination of sugars at low sample volume using UV-Visible quartz cuvette cuvett instead of polarimeter cell. This proposed method could be analysis of sugars with high sample throughput rate and appropriate for analysis of pharmaceutical formulation. This study, the simple determination method by using sample UV-Visible quartz cuvette was developed in order to analyze dextrose, sucrose and lactose. It was found that quartz cuvette was not affected from the sodium light source at wavelength of 589.0 nm and it was possible to adapt for polarimetry technique. The linear calibration curve of dextrose, sucrose and lactose standard solution using polarimeter sample tube were constructed in the concentration ranges of 2.5–15.0 % w/v. Linear regression between the angle of rotation (y) and concentration of each sample (x) were expressed as the equation of y = 1.0941x – 0.1824 (r2= 0.9993), y = 1.3515x –0.1581 (r2= 0.9998) and y= 1.0390x – 0.0162 (r2= 0.9997) for dextrose, sucrose and lactose, respectively. Interestingly, the calibration curve of sugars standard solution using UV-Visible quartz cuvette were shown as y = 0.1050x - 0.1038 (r2= 0.9990), y = 0.1312x – 0.1458 (r2= 0.9989) and y = 0.1072x – 0.0335 (r2= 0.9991) for dextrose, sucrose and lactose, respectively. The detection limits (LOD) of proposed method for determination of dextrose, sucrose and lactose were 0.5, 1.0 and 0.6 % w/v, respectively, while the quantitation limits (LOQ) were 1.6, 3.0 and 1.9 %w/v for anlysis of dextrose, sucrose and lactose, respectively. The interferences study for proposed method from sodium chloride was investigated. It had found that this salt shown none effect for the proposed method. The results acquired the proposed method were compared favorably with those acquired by the reference method at a 95% confidence level with no significant difference (n=10). The developed method had shown accurate, precise, and reproducible. Moreover, this method indicated the possibility of a modified polarimetric method for the quantification of sugars. The method is possible to apply both in simple quality control laboratory and local industrial that involved with pharmaceutical production.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Zaitoun M, Chanem M and Haphoush S. Sugars: Types and their functional properties in food and human health. Inter J Public Health Res. 2018; 6: 93-99.
Cadet F and Offmann B. Direct spectroscopic sucrose determination of raw sugar cane juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997; 45: 166-171. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf960700g
Colinas C, Barrera I and Blanco CAA. Novel correlation for rapid lactose determination in milk by a cryoscopic technique. J. of AOAC Int. 2006; 89: 1581-1584. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/89.6.1581
Knochen M, Pistón M, Salvarrey L and Dol IA. Multicommuted flow system for the determination of dextrose in parenteral and hemodialysis concentrate solutions. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005; 37: 823-828. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2004.11.038
Stroop CJM, Bush C, Marple R and LaCourse WR. Cabohydrate analysis of bacterial polysaccharides by high-pH anion-exchange chromatography and on-line polarimetric determination of absolute configuration. Anal. Biochem. 2002; 303: 176-185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2002.5582
Tewari J and Irudayaraj J. Rapid estimation of pol content in sugarcane juice using FTIR-ATR spectroscopy. Sugar Tech. 2003; 3: 143-148. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943625
Sadd WM, Mohamad Salin NS, Ramzi AS and Salim F. Identification and quantification of fructose, glucose and sucrose in watermelon peel juice. Malaysian J. Anal. Sci. 2020; 24: 382-389.
Zielinski ANF, Braga CM, Demiate IM, Beltrame FL, Nogueira A and Wosiacki G. Developmt and optimization of a HPLC-RI method for the determination of major sugars in apple juice and evaluation of the effect of the ripening stage. Food Sci. Tecnol. 2014; 34: 38-43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612014005000003
Yang J, Rainville P, Liu K and Pointer B. Determination of lactose in low-lactose and lactose - free dairy products using LC-MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021; 100, 103824. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.103824
Wang H, Hu L, Zhou P, Ouyang L, Chen B, Li Y, Chen Y, Zhang Y and Zhou J. Simultaneous determination of fructose, glucose and sucrose by solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to source and adulteration analysis of sucrose in tea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021; 96, 103730. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103730
Pismennõi D, Kiritsenko V, Marhivka J, Kutt ML and Vilu R. Development and optimisation of HILIC-LC-MS Method for determination of carbohydrates in fermentation samples. Molecules. 2021; 26, 3669. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123669
Miller JN and Miller JC. Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry, 6th ed., Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2010.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ผู้นิพนธ์ต้องรับผิดชอบข้อความในบทนิพนธ์ของตน มหาวิทยาลัยพะเยา ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยกับบทความที่ตีพิมพ์เสมอไป ผู้สนใจสามารถคัดลอก และนำไปใช้ได้ แต่จะต้องขออนุมัติเจ้าของ และได้รับการอนุมัติเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรก่อน พร้อมกับมีการอ้างอิงและกล่าวคำขอบคุณให้ถูกต้องด้วย







