Biogenic amine formation and microbiological profile in Asian seabass and short-bodied mackerel during refrigerated storage
Main Article Content
Abstract
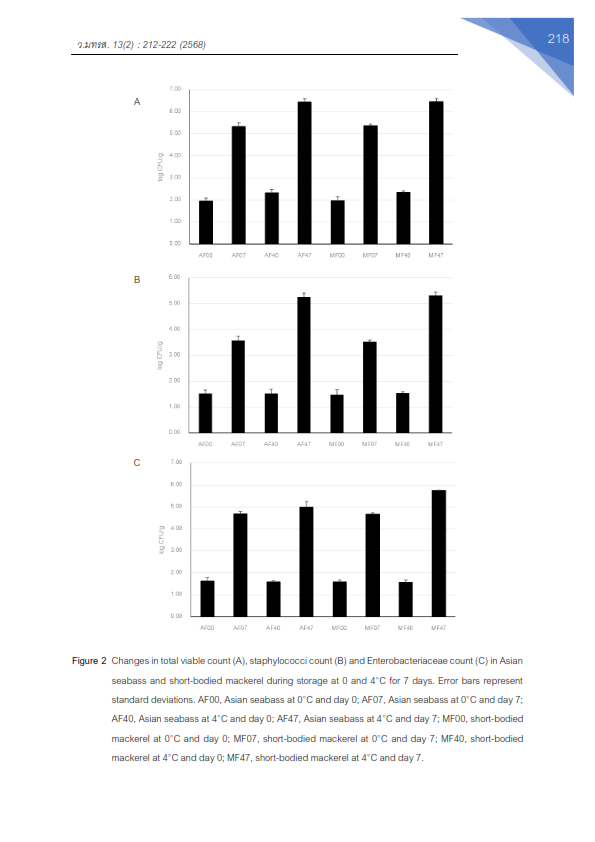
Biogenic amines (BAs) are key chemical indicators of fish spoilage and potential food safety hazards. This study investigated the formation of four common BAs-histamine, cadaverine, putrescine, and tyramine-and monitored microbial populations in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) and short-bodied mackerel (Rastrelliger brachysoma) stored at 0°C and 4°C for 7 days. Total viable bacteria, staphylococci, and Enterobacteriaceae were enumerated using culture-based methods, while BA concentrations were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results revealed that microbial growth was significantly higher (p<0.05) in both fish species stored at 4°C when compared with those stored at ice temperature (0°C). The counts of total viable bacteria, staphylococci, and Enterobacteriaceae of short-bodied mackerel stored at 4°C reached 5.32-6.47 Log CFU/g after 7 days. Histamine levels in short-bodied mackerel stored at 4°C reached 292.67±1.53mg/kg by day 7, exceeding the Codex safety limit of 200mg/kg. Cadaverine, putrescine, and tyramine levels were also increased to 615.00±1.00, 461.67±1.53, and 731.67±1.53mg/kg, respectively. In contrast, histamine remained undetectable in Asian seabass under the same storage conditions. However, cadaverine, putrescine, and tyramine were detected in Asian seabass at 17.67±1.53, 17.00±2.65, and 8.33±2.08mg/kg, respectively. These findings provide essential reference data for assessing spoilage in marine fish species commonly consumed in Thailand and highlight the need for strengthened seafood safety standards on histamine. They further emphasize the critical role of effective cold chain management in traditional markets and local distribution systems.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Published manuscript are the rights of their original owners and RMUTSB Academic Journal. The manuscript content belongs to the authors' idea, it is not the opinion of the journal's committee and not the responsibility of Rajamangala University of Technology Suvarnabhumi
References
Abré, M. G., Kouakou-Kouamé, C. A., N’guessan, F. K., Teyssier, C., & Montet, D. (2023). Occurrence of biogenic amines and their correlation with bacterial communities in the Ivorian traditional fermented fish adjuevan during the storage. Folia Microbiologica, 68(2), 257-275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-022-01010-2
Akkaya, E., Colak, H., Hampikyan, H., Engin, A. S., & Bingol, E. B. (2024). Biogenic amine content and shelf-life of salmon fillets packaged in modified atmospheres of low-level carbon monoxide and different carbon dioxide concentrations. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 74(4), 323-339. https://doi.org/10.31883/pjfns/194650
AOAC International. (2023). Appendix K: Guidelines for dietary supplements and botanicals (pp. 1-32). Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. https://doi.org/10.1093/9780197610145.005.011
Arulkumar, A., Paramithiotis, S., & Paramasivam, S. (2023). Biogenic amines in fresh fish and fishery products and emerging control. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 8(4), 431-450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaf.2021.02.001
Barp, L., Moret, E., & Moret, S. (2024). Evolution of eight biogenic amines in raw and preserved mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets monitored by UHPLC-PDA. Separations, 11(8), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11080235
Çakmak, T., & Sancak, Y. C. (2023). Determination of biogenic amine formation, microbiological and sensory changes in carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) stored at cold (4°C). Van Veterinary Journal, 34(1), 32-42. https://doi.org/10.36483/vanvetj.1209788
Codex Alimentarius (Codex). (2024). Codex General standard for contaminants and toxins in food and feeds (CXS 193-1995). FAO/WHO; Rome. http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B193-1995%252FCXS_193e.pdf
del Rio, B., Redruello, B., Fernandez, M., Martin, M. C., Ladero, V., & Alvarez, M. A. (2020). The biogenic amine tryptamine, unlike β-phenylethylamine, shows in vitro cytotoxicity at concentrations that have been found in foods. Food Chemistry, 331, 127303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127303
El Hariri, O., Bouchriti, N., & Bengueddour, R. (2018). Risk assessment of histamine in chilled, frozen, canned and semi-preserved fish in Morocco: Implementation of risk ranger and recommendations to risk managers. Foods, 7(10), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7100157
Food and Drug Administration. (2019). Guidelines for the validation of chemical methods in food, feed, cosmetics, and veterinary products (3rd ed.). Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC. https://www.fda.gov/science-research/field-science-and-laboratories/method-validation-guidelines
Food and Drug Administration. (2021). Fish and fishery products hazards and controls guidance (4th ed.). Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC. https://www.fda.gov/food/seafood-guidance-documents-regulatory-information/fish-and-fishery-products-hazards-and-controls
Konandana, P., Buangoen, A., & Ingviya, T. (2021). An outbreak of histamine food poisoning after ingestion longtail tuna in prisoners taking isoniazid from Songkhla province prison, Songkhla province, Thailand. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 13(3), 108-118. https://li01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/pnujr/article/view/249371
Li, L., Liu, D., Li, X., Zhang, B., Li, C., Xiao, Z., Liu, M., Fang, F., Deng, N., & Wang, J. (2023). The dynamic changes of microbial diversity and biogenic amines in different parts of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) head during storage at -2°C. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 118, 105228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105228
Li, J., Yang, D., Zhao, Y., Wang, D., Huang, H., & Li, C. (2025). Novel insight into metabolism mechanism of biogenic amines during fermentation of Chinese traditional fermented Mandarin fish (Chouguiyu) based on metabolism pathway and correlation network. Foods, 14(16), 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162863
Morello, S., Lupi, S., Barcucci, E., Fragassi, S., Torres, E., Dosio, D., Marchese, C., Bezzo Llufrio, T., Gili, M., & Bianchi, D. M. (2024). Histamine in fishery: A five-year survey in Northern Italy. Toxins, 16(11), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16110456
Nam, N. N., Do, H. D. K., Loan Trinh, K. T., & Lee, N. Y. (2023). Metagenomics: An effective approach for exploring microbial diversity and functions. Foods, 12(11), 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112140
Ntzimani, A., Papamichail, E., Dermesonlouoglou, E., Tsironi, T., & Taoukis, P. (2024). Shelf life study of chilled mullet (Mugil cephalus): Histamine formation and quality degradation at constant and dynamic storage conditions. Fishes, 9(12), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9120480
Pinto de Rezende, L., Barbosa, J. B., Gomes, A. M., Silva, A. M., Correia, D. F., & Teixeira, P. (2022). Inhibition of several bacterial species isolated from squid and shrimp skewers by different natural edible compounds. Foods, 11(5), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050757
Qu, Y., Wang, J., Liu, Z., Wang, X., & Zhou, H. (2022). Effect of storage temperature and time on biogenic amines in canned seafood. Foods, 11(18), 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182743
Rashid, N., Shafee, M., Iqbal, S., Samad, A., Khan, S. A., Hasni, M. S., Rehman, Z. U., Ullah, S., Rehman, F. U., Khan, G. I., Ahmad, S., & Akbar, A. (2021). Enterotoxigenic methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus contamination in salted fish from Gwadar Balochistan. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 83, e247701. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.247701
Sánchez-Parra, M., Lopez, A., Ordóñez-Díaz, J. L., Rodríguez-Solana, R., Montenegro-Gómez, J. C., Pérez-Aparicio, J., & Moreno-Rojas, J. M. (2024). Evaluation of biogenic amine and free fatty acid profiles during the manufacturing process of traditional dry-cured tuna. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 17(2), 452-463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03134-w
Sivamaruthi, B. S., Kesika, P., & Chaiyasut, C. (2021). A narrative review on biogenic amines in fermented fish and meat products. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(5), 1623-1639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04686-x
Soares, J. M., Gomes, J. M., Reis, G. C., Hoyos, D. C., Custodio, F. B., & Gloria, M. B. A. (2021). Biogenic amines in amazonian fish and their health effects are affected by species and season of capture. Food Control, 123, 107773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107773
Syropoulou, F., Parlapani, F. F., Kakasis, S., Nychas, G. J. E., & Boziaris, I. S. (2021). Primary processing and storage affect the dominant microbiota of fresh and chill-stored sea bass products. Foods, 10(3), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10030671
Tao, Z., Liu, W., Hu, Q., Wu, X., Xie, S., Zhang, H., Fu, M., Yang, J., & Jiang, Y. (2022). Interaction between bacterial diversity and biogenic amines production in a salted mackerel stored at soft frozen (-7°C-0°C) storage. Food Science & Nutrition, 10(2), 412-421. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2647
Tunç, S., Demirhan, B., & Demirhan, B. E. (2025). Investigation of histamine, physicochemical quality, and potential health risks in various canned fish products. Foods, 14(13), 2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132314
Ucar, Y., & Ozogul, F. (2024). Biogenic amines in seafood. Food Bulletin, 3(1), 9-15. https://doi.org/10.61326/foodb.v3i1.258
Visciano, P., Schirone, M., & Paparella, A. (2020). An overview of histamine and other biogenic amines in fish and fish products. Foods, 9(12), 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121795
Yassoralipour, A., Bakar, J., Abdul Rahman, R., & Abu Bakar, F. (2016). Physicochemical properties, microbial profile, and biogenic amines content of Barramundi (Lates calcarifer Bloch) fillets wrapped in selected packaging films under modified atmosphere packaging. International Journal of Food Properties, 19(12), 2707-2717. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1142453
Zhang, X., Chi, H., Peng, D., Jiang, M., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Kang, W., & Li, L. (2025). Integrated metagenomic and LC–MS/MS analysis reveals the biogenic amine-producing strains of two typical Chinese traditional fish products: Fermented Mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) and semi-dried yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Foods, 14(6), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061016