การศึกษาผลกระทบของการแอโนไดเซซั่นสองครั้งต่อประสิทธิภาพของ ท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไซด์สำหรับผลิตเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสง
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
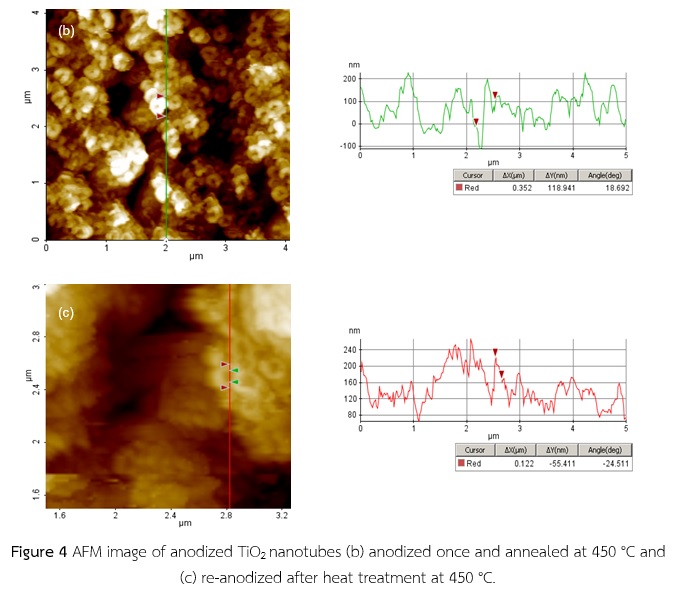
ในงานวิจัยนี้ เราได้สังเคราะห์ท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไชด์บนแผ่นฐานรองไททาเนียมโดยวิธีการ แอโนไดเซซั่นด้วยไฟฟ้ากระแสตรงที่ 50 โวลต์ เพื่อทำเป็นขั้วทำงานสำหรับเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสง (DSSCs) ท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไชด์ถูกสังเคราะห์ในสารละลายอิเล็กโทรไลต์ที่ประกอบด้วยเอทาลีนไกคอล แอมโมเนียฟลูออไรด์ และน้ำบริสุทธิ์เป็นเวลา 3 ชั่วโมง เซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสงถูกประกอบขึ้นโดยการประกบกันระหว่างแผ่นแก้วโปร่งแสงนำไฟฟ้ากับแผ่นขั้วไฟฟ้าท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไซด์ที่ดูดกลืนสีย้อมไวแสง N719 เราศึกษาผลกระทบของการบำบัดความร้อนและการสังเคราะห์สองครั้งต่อประสิทธิภาพของท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไซด์ในเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสงประสิทธิภาพของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสงจากการสังเคราะห์สองครั้งลดลงจาก 3.36% เป็น 0.88% ประสิทธิภาพเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสงที่ทำจากท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไซด์ที่สังเคราะห์แต่ไม่ได้ผ่านการบำบัดความร้อนลดลงเป็น 1.95% กลไกของคู่อิเล็กตรอนและโฮลเคลื่อนย้ายจากแถวของท่อนาโน ไททาเนียมไดออกไซด์สู่ชั้นของออกไซด์และรูพรุนของท่อนาโนไททาเนียมไดออกไซด์ถูกทำลายเมื่อทำการ แอโนไดเซซั่นสองครั้งส่งผลทำให้ประสิทธิภาพของเซลล์แสงอาทิตย์สีย้อมไวแสงต่ำลง
Article Details
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับมหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆในมหาวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว