Application of Greenhouse for Drying Banana with Solar Energy
Main Article Content
Abstract
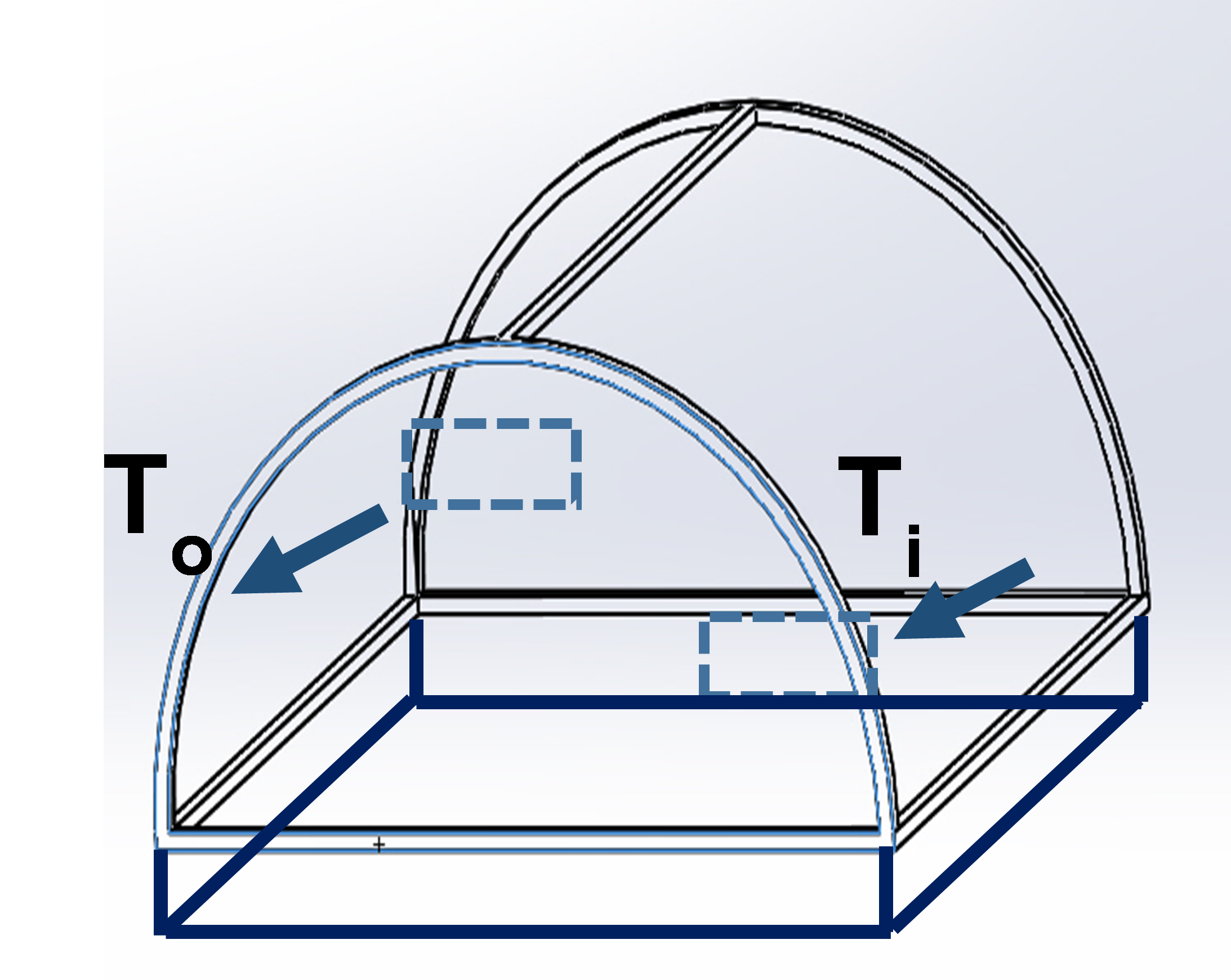
The objective of this research was to adapt a farming greenhouse constructed from polycarbonate sheets for production of solar-dried banana. Two types of drying methods were implemented, (1) the open base method in which the base of the greenhouse was slightly raised from the ground and (2) the closed base method in which a black polyethylene sheet covered the base of the greenhouse to limit the inlet airflow. The drying performance of the two methods were compared to open-air sun drying. The initial moisture content of the banana was 70% (w.b.) and the required final moisture content of the dried banana was 56.5% (w.b.), which is the same as commercially available dried banana. The drying experiments were conducted during 8.00 am - 4.00 pm for 5 days. The closed base greenhouse, open base greenhouse and natural sun drying yielded final moisture contents of 52.8% (w.b.), 58.8% (w.b.) and 59.2% (w.b.), respectively. As the closed base greenhouse was able to provide the lowest relative humidity and highest internal temperature, the highest moisture reduction was obtained. As the environmental conditions inside the open base greenhouse were similar to those of the open-air ambient, the final moisture contents of the bananas from both methods were similar. Drying in the closed base greenhouse resulted in a higher thermal efficiency than drying in the open base greenhouse and open-air sun drying by 29.2% and 34.9%, respectively.
Article Details
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับมหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี และคณาจารย์ท่านอื่นๆในมหาวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว