Comparison of Green Color Stability and Qualities of Singapore Cendol (Lod Chong Singapore) Made from Pandan Leaves (Pandan amaryllifolius Roxb.) Using Sodium Bicarbonate Solution and Lime Water
Main Article Content
Abstract
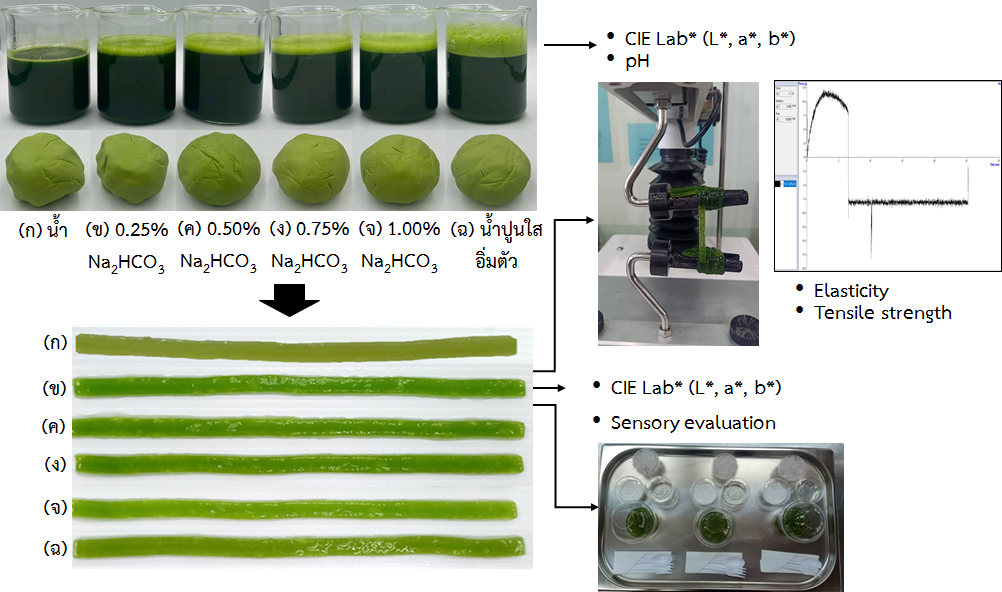
This research investigates the effects of sodium bicarbonate solution and saturated limewater on extracting green pigment from pandan leaves, focusing on color values, texture characteristics, and sensory evaluation of pandan-flavored Singapore cendol (Lod Chong Singapore) to achieve a stable green color and consumer-acceptable quality. The green pigment was extracted from pandan leaves using sodium bicarbonate solution at various concentrations (0.00, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 1.00%) and saturated limewater. The resulting extract was then used in the production of pandan-flavored Singapore cendol noodles. It was found that a 0.25% sodium bicarbonate solution produced Singapore cendol with the highest greenness (-a*), the most stable green color, and superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to other concentrations (p ≤ 0.05). Additionally, this formulation was more similar in quality to samples made with saturated limewater than to those made with other concentrations. Sensory analysis indicated that the pandan-flavored Singapore cendol noodles made with 0.25% sodium bicarbonate solution received the highest acceptance in terms of appearance, color, aroma, taste, texture and overall preference. Therefore, using a 0.25% sodium bicarbonate solution is suitable for extracting green pigment from pandan leaves to produce pandan-flavored Singapore cendol noodles with a stable green color and enhanced physical quality.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชชา มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครศรีธรรมราช ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรง ซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสารไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วยหรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชชา มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครศรีธรรมราช ถือเป็นลิขสิทธ์ของวารสารวิชชา มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครศรีธรรมราช หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำข้อมูลทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อการกระทำการใด ๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรจากวารสารวิชชา มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครศรีธรรมราชก่อนเท่านั้น
The content and information in the article published in Wichcha journal Nakhon Si Thammarat Rajabhat University, It is the opinion and responsibility of the author of the article. The editorial journals do not need to agree. Or share any responsibility.
References
สรรษนีย์ เต็มเปี่ยม วรลักษณ์ ปัญญาธิติพงศ์ และศุภัคษร มาแสวง. (2566). ผลของแป้งสุกในแป้งโดที่มีต่อคุณภาพทางประสาทสัมผัส สี และลักษณะเนื้อสัมผัสของผลิตภัณฑ์ลอดช่องสิงคโปร์ใบเตย. PBRU Science Journal, 20(1), 19-23.
Arshimny, N.A. and Syamsu, K. (2020). Production and characteristic of natural coloring and flavoring preparations from pandan leaves (Pandanus amaryllifolius). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (pp. 012014). Bogor: IOP Publishing.
Aziz, A., Rubinoff, J., Kaur, M. and Cohen, J. (2023). The effect of the sodium bicarbonate buffer on the acidity of hydroponically grown kale. Journal of Dawning Research, 5, 3-20.
Charutigon, C., Jitpupakdree, J., Namsree, P. and Rungsardthong, V. (2008). Effects of processing conditions and the use of modified starch and monoglyceride on some properties of extruded rice vermicelli. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41(4), 642-651, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.04.009.
de Oliveira, A.F. (2020). Buffering function: A general approach for buffer behavior. The Journal of Engineering and Exact Sciences, 6(3), 0387-0396, doi: https://doi.org/10.18540/jcecvl6iss3pp0387-0396.
Dewi, E.N., Purnamayati, L. and Jaswir, I. (2022). Effects of thermal treatments on the characterisation of microencapsulated chlorophyll extract of Caulerpa racemose. International Food Research Journal, 29(6), 1279-1292.
Gandul-Rojas, B. and Gallardo-Guerrero, L. (2014). Pigment changes during processing of green table olive specialities treated with alkali and without fermentation. Food Research International, 65(Part B), 224-230, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.05.007.
Gunawan, M.I. and Barringer, S.A. (2000). Green color degradation of blanched broccoli (Brassica oleracea) due to acid and microbial growth. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 24, 253-263, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4549.2000.tb00417.x.
Han, L., Lu, Z., Hao, X., Cheng, Y. and Li, L. (2012). Impact of calcium hydroxide on the textural properties of buckwheat noodles. Journal of Texture Studies, 43(3), 1-8, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4603.2011.00331.x.
Indrasti, D., Andarwulan, N., Purnomo, E.H. and Wulandari, N. (2018). Stability of chlorophyll as natural colorant: A review for Suji (Dracaena angustifolia Roxb.) leaves’ case. Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science, 6(3), 609-625, doi: https://doi.org/10.12944/CRNFSJ.6.3.04.
Kaewsuksaeng, S. (2011). Chlorophyll degradation in horticultural crops. Walailak Journal of Science and Technology, 8(1), 9-19.
Karim, A.A., Nadiha, M.Z., Chen, F.K., Phuah, Y.P., Chui, Y.M., and Fazilah, A. (2008). Pasting and retrogradation properties of alkali-treated sago (Metroxylon sagu) starch. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(6), 1044-1053, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.05.011.
Koca, N., Karadeniz, F. and Burdurlu, H.S. (2006). Effect of pH on chlorophyll degradation and colour loss in blanched green peas. Food Chemistry, 100(2), 609-615, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.09.079.
Lai, L.N., Karim, A.A., Norziah, M.H. and Seow, C.C. (2004). Effects of Na2CO3 and NaOH on pasting properties of selected native cereal starches. Journal of Food Science, 69(4), 249-256, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.tb06324.x.
Minh, N.P., Vo, T.T., Van Man, L., Phong, T.D., Van Toan, N. and Vo, H.N. (2019). Green pigment extraction from pandan (Pandanus amaryllifolius) and its application in food industry. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 11(3), 925-929.
Ngo, T. and Zhao, Y. (2007). Formation of zinc-chlorophyll-derivative complexes in thermally processed green pears (Pyrus communis L.). Journal of Food Science, 72(7), C397-C404, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00465.x.
Pedcharat, K., Jangchud, K. and Prinyawiwatkul, W. (2021). Physicochemical properties of rice flour as affected by alkaline soaking and washing treatments. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 56(5), 2539-2547, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14892.
Rafiq, S.I., Singh, S., and Saxena, D.C. (2016). Effect of alkali-treatment on physicochemical, pasting, thermal, morphological and structural properties of Horse Chestnut (Aesculus indica) starch. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 10, 676-684, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-016-9351-y.
Ragheb, A.A., Abdel-Thalouth, I. and Tawfik, S. (1995). Gelatinization of starch in aqueous alkaline solutions. Starch/Stärke, 47(9), 338-345, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/star.19950470904.
Rattanapitigorn, P., Ogawa, M. and Rattanapanone, N. (2016). Effect of Methocel™, maltodextrin, sodium chloride, and pH on foaming properties and foam-mat drying of aqueous pandan (Pandanus amaryllifolius) leaves extract. Chiang Mai University Journal of Natural Sciences, 15(3), 237-252.
Senklang, P. and Anprung, P. (2010). Optimizing enzymatic extraction of Zn-chlorophyll derivatives from pandan leaf using response surface methodology. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 34(1), 759-776, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4549.2009.00393.x.
Suryani, C.L.S., Wahyuningsih, T.D., Supriyadi, S. and Santoso, U. (2020). The potential of mature pandan leaves as a source of chlorophyll for natural food colorants. Jurnal Teknologi Dan Industri Pangan, 31(2), 127-137, doi: https://doi.org/10.6066/jtip.2020.31.2.127.
Sytykiewicz, H., Sprawka, I., Czerniewicz, P., Sempruch, C., Leszczynski, B. and Sikora, M. (2013). Biochemical characterization of chlorophyllase from leaves of selected Prunus species-A comparative study. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 60(3), 457-465, doi: https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2013_2007.
Tijskens, L.M.M., Schijvens, E.P.H.M. and Biekman, E.S.A. (2001). Modelling the change in colour of broccoli and green beans during blanching. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2(4), 303-313, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1466-8564(01)00045-5.
Wakte, K.V., Thengane, R.J., Jawali, N. and Nadaf, A.B. (2010). Optimization of HS-SPME conditions for quantification of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and study of other volatiles in Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. Food chemistry, 121(2), 595-600, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.12.056.
Xu, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, C., Ma, M., Sui, Z. and Corke, H. (2024). Effect of mild alkali treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of normal and waxy rice starches. Foods, 13(15), 2-11, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152449.
Zheng, Y., Shi, J., Pan, Z., Cheng, Y., Zhang, Y. and Li, N. (2014). Effect of heat treatment, pH, sugar concentration, and metal ion addition on green color retention in homogenized puree of Thompson seedless grape. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 55(2), 595-603, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.011.