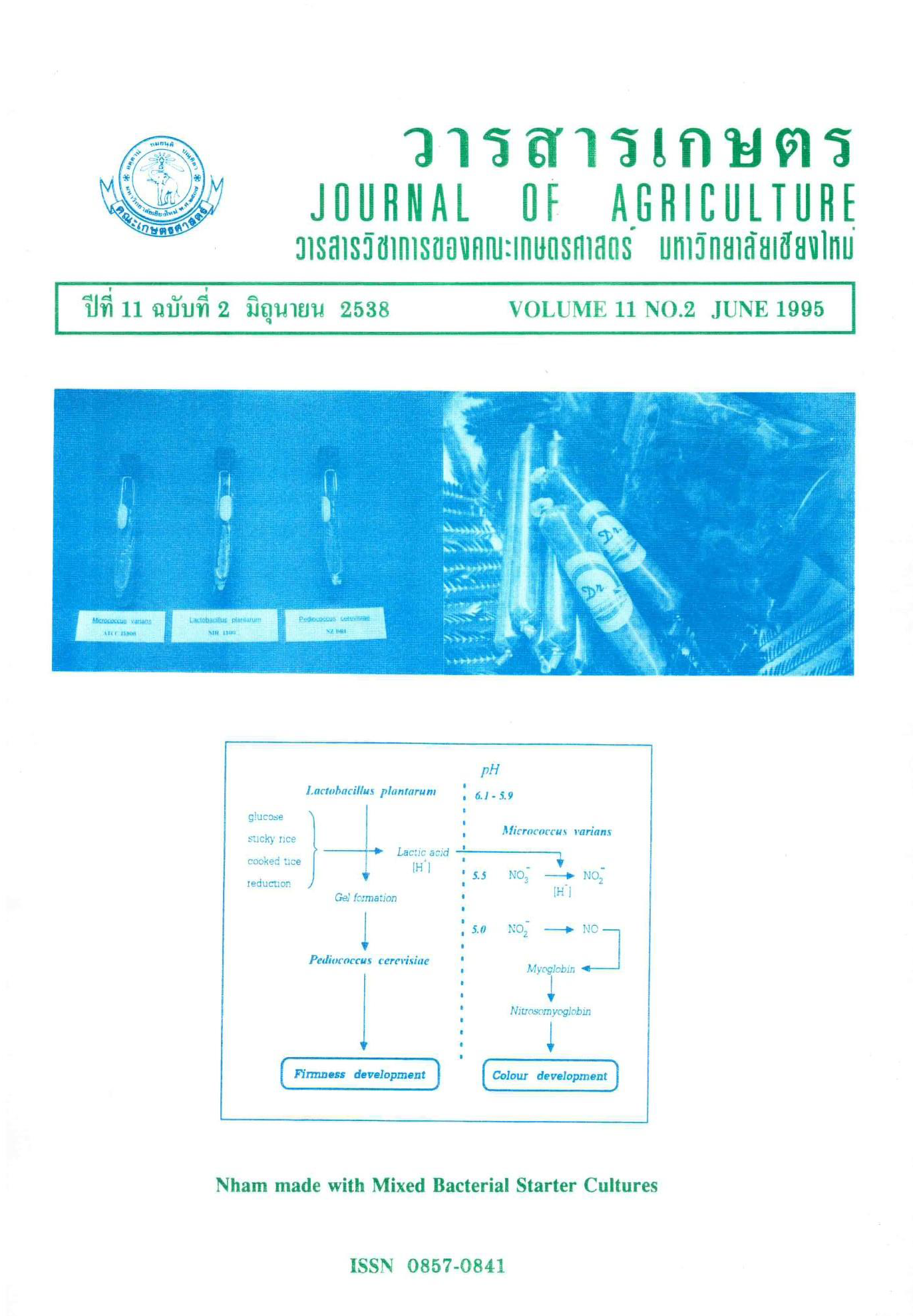
การพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์แหนมโดยใช้เทคโนโลยีเชื้อบริสุทธิ์เริ่มต้นผสม 8. ผลของสารประกอบฟอสเฟตต่อการเจริญเติบโตของเชื้อบริสุทธิ์เริ่มต้นที่ใช้ในการผลิตแหนม
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
สารประกอบฟอสเฟต 3 ประเภท คือ โซเดียมไตรโพลีฟอสเฟต โซเดียมเฮกซาเมตาฟอสเฟต และโซเดียมแอซิดไพโรฟอสเฟต ในระดับร้อยละ 0.3 ได้ถูกศึกษาถึงผลกระทบของสารประกอบดังกล่าวต่อการเจริญเติบโตของเชื้อบริสุทธิ์เริ่มต้นที่ใช้ในการผลิตแหนม โดยทำการศึกษาในระบบอาหารเลี้ยงเชื้อ MRS สำหรับ L. plantarum และ P. cerevisiae และในระบบอาหารเลี้ยงเชื้อ BHI สำหรับ M. varians และทำการเพาะเชื้อดังกล่าวทั้งสามที่อุณหภูมิ 30 องศาเซลเซียส เป็นเวลา 48 ชั่วโมง จากผลการทดลองพบว่า โซเดียมแอซิดไพโรฟอสเฟต และโซเดียมเฮกซาเมตาฟอสเฟต มีผลที่ให้ค่าความเป็นกรดเป็นด่างลดลง และเพิ่มค่าความเป็นกรดทั้งหมดในช่วงแรกของการเพาะเชื้อ ส่วนโซเดียมไตรโพลีฟอสเฟตมีผลเช่นเดียวกับตัวอย่างควบคุม นอกจากนี้ยังพบว่าอัตราการผลิตกรดแลคติคของเชื้อ L. plantrum มีมากกว่า P. cerevisiae อย่างไรก็ตาม สารประกอบฟอสเฟตทั้งสาม ไม่มีผลต่อการเจริญเติบโตของเชื้อ L. plantarum และ P. cerevisiae
อย่างไรก็ตาม สารประกอบฟอสเฟตประเภท โซเดียมแอซิดไพโรฟอสเฟต และโซเดียมเฮกซาเมตาฟอสเฟตมีผลต่อการหยุดชงักการเจริญเติบโตของเชื้อ M. varians อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ P<0.05 ส่วนโซเดียมไตรโพลีฟอสเฟตไม่มีผลต่อการหยุดชงักการเจริญเติบโตของเชื้อดังกล่าว เชื้อ M. varians สามารถเจริญเติบโตปกติ และมีประสิทธิภาพในการรีดิวส์สารไนเตรทเป็นไนไตรท์อย่างดีในระบบอาหารเลี้ยงเชื้อ
Article Details
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Bacus, J. (1984). Utilization of Microorganisms in Meat Processing Research Studies Press, Ltd., England.
Chen, T.C., J.T. Culotta, and W.S. Wang. (1973). Effect of Water and microwave energy pre-cooking on microbial quality of chicken parts. J. Food Sci., 38: 155.
Elliott, R.P., R.P. Straka, and J.A. Garibaldi. (1964). Polyphosphate inhibition of growth of Pseudomonads from poultry meat. Appl. Microbiol., 12:517.
Firstenberg-Eden, R., D.B. Rowley, and G.E. Shattuck. (1981). Inhibition of Moraxella-Acetobacter cells by sodium phosphates and sodium chloride. J. Food Sci., 46: 579.
Foster, R.D., and G.C. Mead.(1976). Effect of temperatures and added polyphosphate on the survival of salmonellae in poultry meat during cold storage. J. Appl. Bacteriol., 41: 505.
Gray, G.W., and S.G. Wilkinson. (1965). The action of ethylene-diaminetetraacetic acid on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 28: 153.
Kohl, W.F. (1971). A new process for pasteurizing egg whites. Food Technol., 25: 1176.
Molins, R.A., A.A. Kraft, D.G, Olson, and D.K. Hotchkiss. (1984). Recovery of selected bacteria in media containing 0.5% Food Grade poly-and pyrophosphates. J. Food Sci., 49: 948.
Post, F.J., G.B. Krishnamurty, and M.D. Flanagan (1963). Influence of sodium hexametaphosphate on selected bacteria. Appl. Microbiol., 11: 430.
Spencer, J.V., and L.E. Smith.(1962). The effect of chilling chicken fryers in a solution of polyphosphates upon moisture uptake, microbial spoilage, tenderness, juiciness and flavour. Poultry Sci., 41: 1685.
Steinhauer, J.E., and G.J. Banwart. (1964). The effect of food grade polyphosphates on the microbial
population of chicken meat. Poultry Sci., 43: 618.
Walonick, D.S. (1987). Stat-Packets. Walonick Associates Inc., Minneapoils, MN.
Wagner, M.K., and F.F. Busta,. (1983). Effect of sodium acid pyrophosphate in combination with sodium nitrate or sodium nitrite/potassium sorbate on Clostridium botulinum growth and toxin production in beef/pork frankfurter emulsion. J. Food Sci., 48: 990.